Foot and toe fractures: Difference between revisions
Mceledon83 (talk | contribs) |
Mceledon83 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
===Fifth Metatarsal=== | ===Fifth Metatarsal=== | ||
====Background==== | ====Background==== | ||
Os peroneum is an accessory bone (ossicle)located at the lateral side of the tarsal cuboid, proximal to the base of 5th metatarsal, commonly mistaken for fx | *Os peroneum is an accessory bone (ossicle)located at the lateral side of the tarsal cuboid, proximal to the base of 5th metatarsal, commonly mistaken for fx | ||
3 types of fractures: | *3 types of fractures: | ||
#Tuberosity (styloid) avulsion fracture | #Tuberosity (styloid) avulsion fracture | ||
##Most common fx at base of 5th metatarsal | ##Most common fx at base of 5th metatarsal | ||
Revision as of 04:29, 22 August 2013
Hindfoot
Talus
Background
- Almost always associated with other injuries
Diagnosis
- CT often required for accurate diagnosis
Management
- Major fracture (talar neck and head)
- Immediate ortho consultation required (high rate of avascular necrosis)
- Minor fracture
- Posterior splint, NWB, ortho referral
Calcaneus
Background
- Associated injuries are common
- Types
- Intra-articular (75%)
- Sclerotic line may be only evidence of impacted fracture
- Extra-articular (25%)
- Anterior process fx is most common
- Intra-articular (75%)
Diagnosis
- Imaging
- Decreased Boehler's angle (<25') may be only sign of fx (compare w/ opposite side)
Treatment
- Intra-articular fracture
- Immobilization w/ posterior splint
- Non-weightbearing
- Elevation (very important - fx has high rate of severe swelling)
- Ortho consult
- Extra-articular fracture
- Immobilization and close ortho f/u
Images
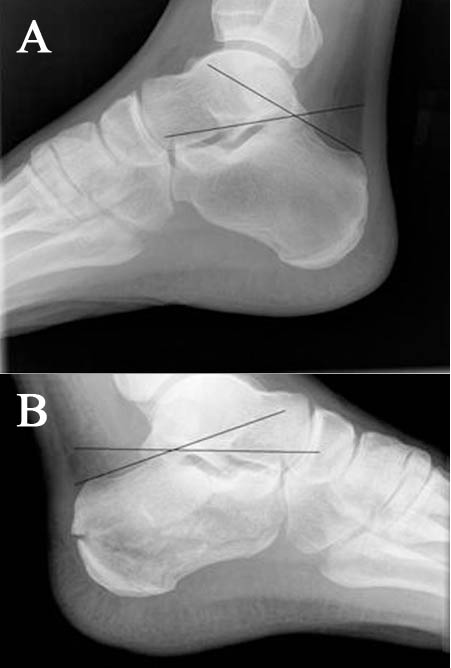
- (A) Normal Boehler's angle and (B) Abnormal Boehler's angle
Midfoot
LisFranc Injury
- See Lisfranc Injury
- All are diagnosed/managed in similar way
- Imaging: (weight-bearing AP, lateral, oblique)
- CT sometimes necessary
- Treatment: Non-weightbearing short leg cast, ortho referral
- Imaging: (weight-bearing AP, lateral, oblique)
Forefoot
Fifth Metatarsal
Background
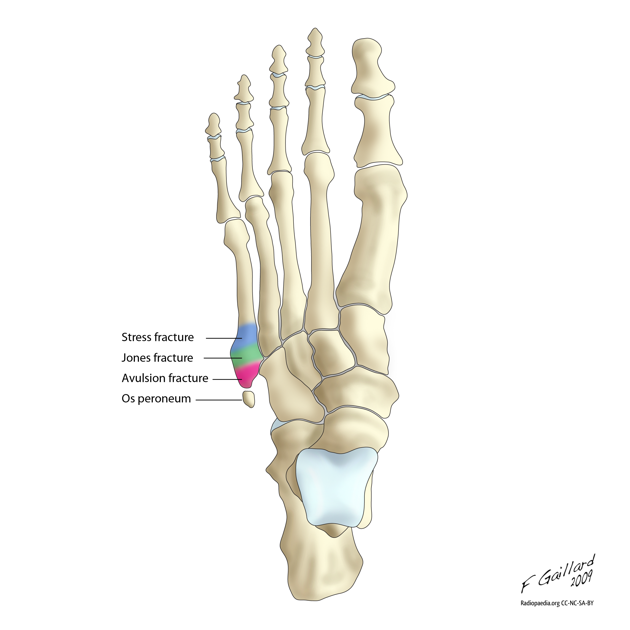
- Os peroneum is an accessory bone (ossicle)located at the lateral side of the tarsal cuboid, proximal to the base of 5th metatarsal, commonly mistaken for fx
- 3 types of fractures:
- Tuberosity (styloid) avulsion fracture
- Most common fx at base of 5th metatarsal
- Sx often mild, pts usually present with sprained ankle complaint
- Occurs due to forced inversion foot/ankle while in plantar flexion
- Jones or metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction fracture
- Abrupt onset of lateral foot pain, with no prior h/o pain at that site, suggests acute injury and helps distinguish from stress injury
- Occurs due to sudden change in direction w/ heel off the ground
- Edema & ecchymosis usually present, may not be able to bear weight
- Diaphyseal stress fracture
- Occurs through repetitive microtrauma
- Ask about persistent pain prior to acute event to help distinguish stress fx from acute fx (sometimes sx of stress fx will worsen after acute stress and mislead you into thinking acute fx)
Diagnosis
Plain radiographs are usually adequate
- Must distinguish Jones fx from diaphyseal stress freacture
Management
- Tuberosity (Styloid) Avulsion Fracture
- Refer to ortho if > 3mm displacement
- Nondisplaced fx usually require only symptomatic tx, RICE
- Walking boot (casting rarely necessary) and weight-bearing as tolerated, f/u in 1 week
- Jones Fracture (non-displaced)
- Posterior splinting, NWB, RICE, ortho f/u in 3-5 days
- 50% of Jones fx treated conservatively may result in nonunion or refracture
- Conservative tx failure usually due to poor vascular supply of bone and premature return to weight-bearing
- Diaphyseal Stress Fracture
- Ortho referral
Metatarsal
Background
- Must rule-out associated Lisfranc injury
Management
- Posterior splint, NWB, ortho referral in 2-3d
Phalange
- Management: buddy-taping, hard-soled shoe
See Also
Source
- Tintinalli
- Ilustration by Dr. Frank Gaillard; CC SA NC BY licence
- http://radiopaedia.org/articles/jones_fracture