Cervical spinous process fracture: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
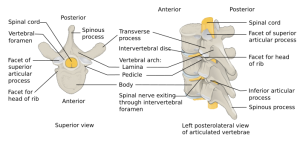
*Also known as " | *Isolated fracture of the spinous processes of the lower cervical or upper thoracic vertebrae | ||
**Caused by hyperflexion of neck → muscles pull on supraspinous ligament → avulsion fracture of spinous process | |||
*Also known as "clay shoveler's" fracture | |||
*A [[Unstable spine fractures|"stable"]] fracture | *A [[Unstable spine fractures|"stable"]] fracture | ||
*C7 is most commonly affected | |||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
* | *Pain in lower neck/upper back | ||
* | *Tenderness over fracture site | ||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 14: | ||
==Evaluation== | ==Evaluation== | ||
* | *Plain films or CT of cervical/thoracic spine | ||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
*Prehospital Immobilization see [[EBQ:Prehospital Spine Immobilization|NAEMSP National Guidelines for Spinal Immobilization]] | *Prehospital Immobilization see [[EBQ:Prehospital Spine Immobilization|NAEMSP National Guidelines for Spinal Immobilization]] | ||
* | *Place in cervical collar - high rates of union with conservative management | ||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
* | *Discharge | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Cervical spine injuries]] | *[[Cervical spine injuries]] | ||
==References== | |||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:Trauma]] | [[Category:Trauma]] | ||
[[Category:Orthopedics]] | [[Category:Orthopedics]] | ||
Revision as of 04:02, 5 June 2017
Background
- Isolated fracture of the spinous processes of the lower cervical or upper thoracic vertebrae
- Caused by hyperflexion of neck → muscles pull on supraspinous ligament → avulsion fracture of spinous process
- Also known as "clay shoveler's" fracture
- A "stable" fracture
- C7 is most commonly affected
Clinical Features
- Pain in lower neck/upper back
- Tenderness over fracture site
Differential Diagnosis
Vertebral fractures and dislocations types
- Cervical fractures and dislocations
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
Evaluation
- Plain films or CT of cervical/thoracic spine
Management
- Prehospital Immobilization see NAEMSP National Guidelines for Spinal Immobilization
- Place in cervical collar - high rates of union with conservative management
Disposition
- Discharge