Hidradenitis suppurativa: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "==Background== Hidradenitis suppurativa is an inflammatory condition involving the apocrine gland-bearing areas of skin, characterized by recurrent painful draining nodules.<r...") |
Spenceemmett (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
*Inflammatory condition involving the apocrine gland-bearing areas of skin, characterized by recurrent painful draining nodules.<ref>Morrell D, Bowers E. Skin disorders: Groin and skinfolds. In Tintinalli J,ed. Tintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide (8th ed). New York: McGraw Hill Medical; 2011: 1669-70.</ref> | |||
*More common in women and black or biracial individuals.<ref>Garg A, et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:760–4.</ref> | |||
*Rarely occurs before puberty. Peak age of onset is 11–20 yo in women and 21–30 yo in men.<ref>Palmer R, Keefe M. Clin Dermatol. 2001;26:501–3.</ref> | |||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
Revision as of 01:12, 19 August 2020
Background
- Inflammatory condition involving the apocrine gland-bearing areas of skin, characterized by recurrent painful draining nodules.[1]
- More common in women and black or biracial individuals.[2]
- Rarely occurs before puberty. Peak age of onset is 11–20 yo in women and 21–30 yo in men.[3]
Clinical Features
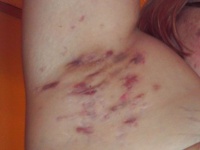
- Tender, nodular lesions most often in the axillae (can also affect gluteal folds, inframammary areas, perianal area, and pubic/genitofemoral areas)
- Malodorous drainage
- Pruritis
- Burning
- Erythema
- Hyperhidrosis
- Scarring[4]
Differential Diagnosis
- Carbuncle
- Furuncle
- Epidermoid or dermoid cyst
- Erysipelas
- Granuloma inguinale
- Lymphogranuloma venereum
- Pilonidal cyst
- Tuberculosis (tuberculous inflammation of the skin)
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis: skin nodules in characteristic sites, may have malodorous drainage
- Diagnosis may be difficult in the ED if single nodule is present.
Management
- Clindamycin 1% topic
- Antibacterial soaps
- Systemic treatments (typically prescribed by specialist): acitretin, finasteride, prednisone
- Incision and drainage should be avoided if possible due to risk of scarring[5]
Disposition
- Discharge with primary care/dermatology followup
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Morrell D, Bowers E. Skin disorders: Groin and skinfolds. In Tintinalli J,ed. Tintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide (8th ed). New York: McGraw Hill Medical; 2011: 1669-70.
- ↑ Garg A, et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:760–4.
- ↑ Palmer R, Keefe M. Clin Dermatol. 2001;26:501–3.
- ↑ *Shah, N. Hidradenitis suppurativa: A treatment challenge. Am Fam Physician. 2005 Oct 15;72(8):1547-1552.
- ↑ Morrell D, Bowers E. Skin disorders: Groin and skinfolds. In Tintinalli J,ed. Tintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide (8th ed). New York: McGraw Hill Medical; 2011: 1669-70.