The difficult airway: Difference between revisions
m (Rossdonaldson1 moved page Difficult Airway Algorithm to Difficult airway algorithm) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==LEMON Mnemonic== | ==LEMON Mnemonic== | ||
===LOOK=== | ===LOOK=== | ||
*Look at the patient externally for characteristics that are known to cause difficult laryngoscopy, | *Look at the patient externally for characteristics that are known to cause difficult laryngoscopy, intubation or ventilation<ref> Rennie LM, Dunn MJG, et al. Is the ‘LEMON’ method an easily applied emergency airway assessment tool? European Journal of Emergency Medicine 2004;11:154–7</ref> | ||
intubation or ventilation<ref> Rennie LM, Dunn MJG, et al. Is the ‘LEMON’ method an easily applied emergency airway assessment tool? European Journal of Emergency Medicine 2004;11:154–7</ref> | |||
*Trauma | |||
*Short neck | |||
*Micrognathia | |||
*Prior surgery | |||
*May also be difficult to bag | |||
**Body mass index | |||
**Advanced age | |||
**Beard | |||
**No teeth | |||
**Snoring | |||
**Dentures | |||
===Evaluate 3-3-2-1 === | ===Evaluate 3-3-2-1 === | ||
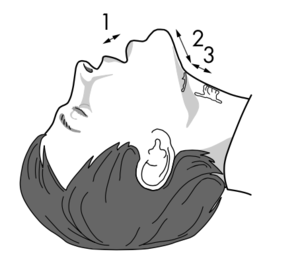
*Ideally the distance between the patient's incisor teeth should be at least 3 finger breadths | * 3 - Ideally the distance between the patient's incisor teeth should be at least 3 finger breadths | ||
* 3 - Distance between the hyoid bone and the chin should be at least 3 finger breadths | |||
* 2 - Distance between the thyroid notch and the floor of the mouth should be at least 2 finger breadths | |||
* 1 - Lower jaw should not sublux more than 1cm | |||
===Mallampati=== | ===Mallampati=== | ||
*The patient sits upright, opens mouth and protrudes tongue | *The patient sits upright, opens mouth and protrudes tongue | ||
*Grades are based on visibility of the uvula, posterior pharynx, hard, and soft palate | *Grades are based on visibility of the uvula, posterior pharynx, hard, and soft palate | ||
===Obstruction=== | ===Obstruction=== | ||
*Assess for conditions leading to airway obstruction such as | *Assess for conditions leading to airway obstruction such as [[Peritonsillar Abscess (PTA)]], trauma, or [[Epiglottitis]]. | ||
===Neck Mobility=== | ===Neck Mobility=== | ||
*Patient places | *Patient places chin down onto their chest and extend their neck. | ||
*Remove the hard collar and provide manual stabilization in trauma patients. | |||
*Poor neck mobility impacts ability to have airway access alignment. | |||
[[File:Mallampati Score.png|thumb|Mallampati Score]] | [[File:Mallampati Score.png|thumb|Mallampati Score]] | ||
| Line 29: | Line 37: | ||
==ASA | ==ASA Difficult Airway Algorithm== | ||
*Does not necessary apply to the | *Does not necessary apply to the ED since the patient can always be awakened and case cancelled | ||
**[[Cricothyrotomy]] should always be the last step in patients with failure to oxygen and ventilate with BVM and inability to intubate | |||
**Straight blade- Miller- may offer better manipulation of a large epiglottis in children or for micrognathia or "buck teeth" | |||
==Airway Adjuncts== | ==Airway Adjuncts== | ||
===Gum Bougie=== | ===Gum Bougie=== | ||
Blind orotracheal intubation | *Blind orotracheal intubation | ||
===Blind Naso Trach Intubation=== | ===Blind Naso Trach Intubation=== | ||
*Not as successful but still an option | |||
*Higher complication rate - bleeding, emesis, and airway trauma | |||
'''Do not attempt in patients with posterior pharyngeal swelling such as in | **'''Do not attempt in patients with posterior pharyngeal swelling such as in [[Angioedema (Upper Airway)]]''' | ||
===Lighted Optical Stylets=== | ===Lighted Optical Stylets=== | ||
*High success rate - esp good for trauma, c-spine precautions | |||
*Use for both reg and nasotrach | |||
*Lower complication rate | |||
*Limited by fogging, secretion, recognition of anatomy, cost, and rare provider experience | |||
===[[LMA]]=== | ===[[LMA]]=== | ||
*Can use without muscle relaxants | |||
*Better than face mask | |||
*Can be used as bridge to fiberoptic intubation | |||
*Limited by unreliable seal at peak insp pressure | |||
*Aspiration risk | |||
*Mucosal trauma | |||
*LMA better than endotracheal for paramedics, especially in pediatric patients<ref>Zhu X-Y, Lin B-C, Zhang Q-S, Ye H-M, Yu R-J. A prospective evaluation of the efficacy of the laryngeal mask airway during neonatal resuscitation. Resuscitation. 2011;82(11):1405–1409. doi:10.1016/j.resuscitation.2011.06.010</ref><ref>Calkins MD, Robinson TD. Combat trauma airway management: endotracheal intubation versus laryngeal mask airway versus combitube use by Navy SEAL and Reconnaissance combat corpsmen. J Trauma. 1999;46(5):927–932</ref> | |||
*Intubating LMA (LMA-Fastrach) provides the opportunity to convert to a definitive airway after rescue with the supraglottic device | |||
===Combitube- esoph obturator=== | ===Combitube- esoph obturator=== | ||
*Good for nurses and paramedics with limited intubation skill | |||
*Indicated if difficult airway predicted: can't see glottis with laryngoscope | |||
*Reduced risk for aspiration compared to face mask or LMA | |||
*Can maintain spinal immobilization | |||
*Large size predisposes to esophogeal dilatation and laceration as a complication | |||
===Trans | ===Trans Tracheal Jet Vent=== | ||
*TTJV | |||
*Needle through cricoid membrane, connected to 50 psi 02- can ventilate and oxygenate ok | |||
*Need adequate oxygen pressure | |||
*1 sec insp and 2- 3 sec exp to avoid breath stacking | |||
*May cause pneumothorax or barotrauma | |||
*Contraindications | |||
**Distorted anatomy | |||
**Bleeding diathesis | |||
**Complete airway obstruction | |||
===Retrograde Intubation=== | ===Retrograde Intubation=== | ||
*Percutaneous guide wire through cricoid and retrograde intubation over wire | |||
*Use guide catheter over wire and then ett | |||
*Need time to set up | |||
*Risk hematoma, pneumothorax | |||
*Contraindicated | |||
**Bleeding | |||
**Distorted anatomy | |||
===Fiberoptic Bronchoscopic Intubation=== | ===Fiberoptic Bronchoscopic Intubation=== | ||
*Takes time to set up | |||
*Good for c-spine injury or awake pt with diff airway | |||
*Go through nose | |||
*Use for all ages, can give 02 during procedure thru fiberscope, immediate confirmation of position | |||
*Limited by secretions, bleeding, poor suction, | |||
===Rigid Fiberoptic Laryngoscopes=== | ===Rigid Fiberoptic Laryngoscopes=== | ||
*Use for diff airway or spinal immobolization | |||
*Not as good and longer time to intubate than flex scope | |||
==Improving Passive Oxygenation== | ==Improving Passive Oxygenation== | ||
*Use in overweight, poor O2 reserve, hypoxia at baseline, concerns for rapid progression to hypoxia once apnea | |||
*Pre-oxygenate while sitting upright, only lay back once RSI drugs pushed. | |||
*30 degrees reverse trendelenburg position for intubation | |||
*Nasal O2 while pre oxygenating and DURING intubation (after induction increase to 15L) | |||
==Surgical Airway== | ==Surgical Airway== | ||
*Can get subglottic stenosis | |||
*Rapid 4 step procedure faster but higher complication rate - cric cart fx | |||
*Can also do wire guided | |||
*Long term morbid, mortality similar to tracheostomy | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
{{Related Difficult Airway Pages}} | {{Related Difficult Airway Pages}} | ||
[[Needle Cricothyrotomy]] | |||
== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Airway/Resus]] | [[Category:Airway/Resus]] | ||
[[Category:Critical Care]] | [[Category:Critical Care]] | ||
Revision as of 22:52, 8 April 2015
LEMON Mnemonic
LOOK
- Look at the patient externally for characteristics that are known to cause difficult laryngoscopy, intubation or ventilation[1]
- Trauma
- Short neck
- Micrognathia
- Prior surgery
- May also be difficult to bag
- Body mass index
- Advanced age
- Beard
- No teeth
- Snoring
- Dentures
Evaluate 3-3-2-1
- 3 - Ideally the distance between the patient's incisor teeth should be at least 3 finger breadths
- 3 - Distance between the hyoid bone and the chin should be at least 3 finger breadths
- 2 - Distance between the thyroid notch and the floor of the mouth should be at least 2 finger breadths
- 1 - Lower jaw should not sublux more than 1cm
Mallampati
- The patient sits upright, opens mouth and protrudes tongue
- Grades are based on visibility of the uvula, posterior pharynx, hard, and soft palate
Obstruction
- Assess for conditions leading to airway obstruction such as Peritonsillar Abscess (PTA), trauma, or Epiglottitis.
Neck Mobility
- Patient places chin down onto their chest and extend their neck.
- Remove the hard collar and provide manual stabilization in trauma patients.
- Poor neck mobility impacts ability to have airway access alignment.
ASA Difficult Airway Algorithm
- Does not necessary apply to the ED since the patient can always be awakened and case cancelled
- Cricothyrotomy should always be the last step in patients with failure to oxygen and ventilate with BVM and inability to intubate
- Straight blade- Miller- may offer better manipulation of a large epiglottis in children or for micrognathia or "buck teeth"
Airway Adjuncts
Gum Bougie
- Blind orotracheal intubation
Blind Naso Trach Intubation
- Not as successful but still an option
- Higher complication rate - bleeding, emesis, and airway trauma
- Do not attempt in patients with posterior pharyngeal swelling such as in Angioedema (Upper Airway)
Lighted Optical Stylets
- High success rate - esp good for trauma, c-spine precautions
- Use for both reg and nasotrach
- Lower complication rate
- Limited by fogging, secretion, recognition of anatomy, cost, and rare provider experience
LMA
- Can use without muscle relaxants
- Better than face mask
- Can be used as bridge to fiberoptic intubation
- Limited by unreliable seal at peak insp pressure
- Aspiration risk
- Mucosal trauma
- LMA better than endotracheal for paramedics, especially in pediatric patients[2][3]
- Intubating LMA (LMA-Fastrach) provides the opportunity to convert to a definitive airway after rescue with the supraglottic device
Combitube- esoph obturator
- Good for nurses and paramedics with limited intubation skill
- Indicated if difficult airway predicted: can't see glottis with laryngoscope
- Reduced risk for aspiration compared to face mask or LMA
- Can maintain spinal immobilization
- Large size predisposes to esophogeal dilatation and laceration as a complication
Trans Tracheal Jet Vent
- TTJV
- Needle through cricoid membrane, connected to 50 psi 02- can ventilate and oxygenate ok
- Need adequate oxygen pressure
- 1 sec insp and 2- 3 sec exp to avoid breath stacking
- May cause pneumothorax or barotrauma
- Contraindications
- Distorted anatomy
- Bleeding diathesis
- Complete airway obstruction
Retrograde Intubation
- Percutaneous guide wire through cricoid and retrograde intubation over wire
- Use guide catheter over wire and then ett
- Need time to set up
- Risk hematoma, pneumothorax
- Contraindicated
- Bleeding
- Distorted anatomy
Fiberoptic Bronchoscopic Intubation
- Takes time to set up
- Good for c-spine injury or awake pt with diff airway
- Go through nose
- Use for all ages, can give 02 during procedure thru fiberscope, immediate confirmation of position
- Limited by secretions, bleeding, poor suction,
Rigid Fiberoptic Laryngoscopes
- Use for diff airway or spinal immobolization
- Not as good and longer time to intubate than flex scope
Improving Passive Oxygenation
- Use in overweight, poor O2 reserve, hypoxia at baseline, concerns for rapid progression to hypoxia once apnea
- Pre-oxygenate while sitting upright, only lay back once RSI drugs pushed.
- 30 degrees reverse trendelenburg position for intubation
- Nasal O2 while pre oxygenating and DURING intubation (after induction increase to 15L)
Surgical Airway
- Can get subglottic stenosis
- Rapid 4 step procedure faster but higher complication rate - cric cart fx
- Can also do wire guided
- Long term morbid, mortality similar to tracheostomy
See Also
Airway Pages
- Pre-intubation
- Induction
- Intubation
- Surgical airways
- Post-intubation
References
- ↑ Rennie LM, Dunn MJG, et al. Is the ‘LEMON’ method an easily applied emergency airway assessment tool? European Journal of Emergency Medicine 2004;11:154–7
- ↑ Zhu X-Y, Lin B-C, Zhang Q-S, Ye H-M, Yu R-J. A prospective evaluation of the efficacy of the laryngeal mask airway during neonatal resuscitation. Resuscitation. 2011;82(11):1405–1409. doi:10.1016/j.resuscitation.2011.06.010
- ↑ Calkins MD, Robinson TD. Combat trauma airway management: endotracheal intubation versus laryngeal mask airway versus combitube use by Navy SEAL and Reconnaissance combat corpsmen. J Trauma. 1999;46(5):927–932