Hypokalemia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Low! = <2.5meq/L | Low! = <2.5meq/L | ||
==Diagnosis== | == Diagnosis == | ||
*CNS | |||
**Weakness | *CNS | ||
**Cramps | **Weakness | ||
**Hyporeflexia | **Cramps | ||
*GI | **Hyporeflexia | ||
**Ileus | *GI | ||
*Renal | **Ileus | ||
**Met alkalosis | *Renal | ||
*CV | **Met alkalosis | ||
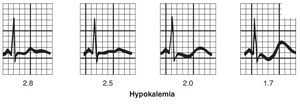
**ECG findings: | *CV | ||
***ST seg depression | **ECG findings: | ||
***U wave (V4-V6) | ***ST seg depression | ||
**Also may cause: | ***U wave (V4-V6)[[Image:ECG Hypokalemia.jpg|thumb|ECG Hypokalemia.jpg]] | ||
**Also may cause: | |||
***PACs/PVCs | ***PACs/PVCs | ||
***Bradycardia or atrial/junctional tachycardia | ***Bradycardia or atrial/junctional tachycardia | ||
***AV block | ***AV block | ||
***V tach, V fib | ***V tach, V fib | ||
Revision as of 00:42, 28 August 2011
Background
Low = <3.5meq/L
Low! = <2.5meq/L
Diagnosis
- CNS
- Weakness
- Cramps
- Hyporeflexia
- GI
- Ileus
- Renal
- Met alkalosis
- CV
- ECG findings:
- ST seg depression
- U wave (V4-V6)
- Also may cause:
- PACs/PVCs
- Bradycardia or atrial/junctional tachycardia
- AV block
- V tach, V fib
- ECG findings:
DDX
- Shift
- Alkalosis (each 0.10 rise in pH causes 0.5 decrease)
- Insulin
- B-agonist
- Decreased intake
- Increased loss
- GI (v/d/fistula)
- Renal
- Diuretics
- Hyperaldo
- Exercise
- HyperCa
- HypoMg
- Drugs
- PCN
- Lithium
- L-dopa
- Theophyline
Treatment
- 20meq/hr KCl IV or PO
- every 10meq should inc serum by ~0.1meq/L
- Treat hypomag if present
Source
Tintinalli