Scapholunate dissociation: Difference between revisions
(→Images) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
*[[File:Scapholunate Dissociation.jpg]] | *[[File:Scapholunate Dissociation.jpg]] | ||
*Dorsal intercalated segment instability | *Dorsal intercalated segment instability | ||
*[[File: | *[[File:Dorsal_Intercalated_Segment_Instability]] | ||
==Source== | ==Source== | ||
Revision as of 22:13, 2 February 2012
Background
- Most commonly injured ligament of the wrist
- Injury most commonly occurs from FOOSH
Clinical Features
- Pain/swelling on radial side of wrist
- "Clicking" sensation with wrist movement
Diagnosis
- Imaging
- A grip compression view or motion study may be necessary in addition to PA/lateral views
- Any of the following signs may be seen:
- Widening of the scapholunate joint space >3mm
- Rotary subluxation of the scaphoid
- Lateral view: Scapholunate angle >60 degrees
- PA view: Cortical ring sign (circular cortex of the bone is more prominent)
- Dorsal intercalated segment instability
- Dorsal angulation of lunate relative to radius resulting in capitolunate angle > 20°
- Seen as loss of the normal collinear arrangement of the capitate, lunate, and radius
Treatment
- Radial gutter splint or short arm volar posterior mold
- Ortho referral
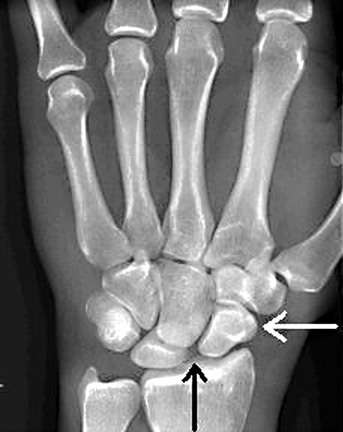
Images
- Black arrow: Scapholunate joint space widening
- White arrow: Cortical ring sign
- Dorsal intercalated segment instability
- File:Dorsal Intercalated Segment Instability
Source
- Tintinalli


