Thoracic burst fracture: Difference between revisions
Ostermayer (talk | contribs) (Text replacement - "Category:Ortho" to "Category:Orthopedics") |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
* Unstable | *Unstable (usually) | ||
* Can occur with or without injury to posterior elements (posterior involvement increases risk for neuro deficits) | |||
* Be certain not to mistakenly call a burst fracture a wedge fracture | *Mechanism: axial loading with flexion compromising anterior and middle column | ||
*Retropulsion of bone causes damage to the spinal canal and neurologic deficits that often cause stable neurologic deterioration. | |||
*Can occur with or without injury to posterior elements (posterior involvement increases risk for neuro deficits) | |||
*Be certain not to mistakenly call a burst fracture a wedge fracture | |||
{{Vertebral fractures and dislocations types}} | |||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 18: | ||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
*Consult Orthopedics or Neurosurgery (Institution dependent) | |||
*Depending on neurologic symptoms and features of the fracture- can be managed nonoperatively | |||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 29: | ||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Orthopedics]] | [[Category:Orthopedics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:36, 24 October 2020
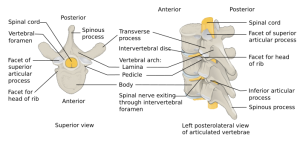
Background
- Unstable (usually)
- Mechanism: axial loading with flexion compromising anterior and middle column
- Retropulsion of bone causes damage to the spinal canal and neurologic deficits that often cause stable neurologic deterioration.
- Can occur with or without injury to posterior elements (posterior involvement increases risk for neuro deficits)
- Be certain not to mistakenly call a burst fracture a wedge fracture
Vertebral fractures and dislocations types
- Cervical fractures and dislocations
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
Clinical Features
Differential Diagnosis
Thoracic Trauma
- Airway/Pulmonary
- Cardiac/Vascular
- Musculoskeletal
- Other
Workup
- Obtain CT if unsure (vs. wedge)
Management
- Consult Orthopedics or Neurosurgery (Institution dependent)
- Depending on neurologic symptoms and features of the fracture- can be managed nonoperatively