Chance fracture: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(→Workup) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
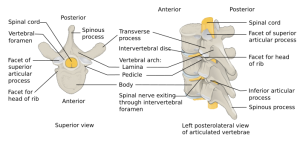
* | *Unstable spinal fracture | ||
* | **Extends horizontally posterior to anterior through the spinous process, pedicles, vertebral body | ||
* | *Caused by flexion-distraction forces; ex. seatbelt use in MVC | ||
**Upon deceleration, the spine forcibly flexes over the seatbelt, distracting (pulling apart) the middle/posterior column of spine | |||
**Most common at T12-L2 due to spinal curvature and mechanism | |||
*Incidence of concurrent intra-abdominal hollow viscus injuries is 50%<ref>Koay J, Davis DD, Hogg JP. Chance Fractures. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536926/</ref> | |||
**Ex. bowel perforations and mesenteric lacerations | |||
**Intra-abdominal injuries more commonly associated than neuro deficits | |||
*May be misdiagnosed as anterior compression fracture (usually stable) | |||
{{Vertebral fractures and dislocations types}} | |||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
* | *Back pain and thoracolumbar midline spinal tenderness to palpation | ||
* | *Seatbelt sign: ecchymosis across the abdominal wall in the location of a lap belt<ref>Huecker MR, Chapman J. Seat Belt Injury. [Updated 2023 Apr 9]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470262/</ref> | ||
* | *Abdominal pain | ||
*Lower extremity neurological deficits | |||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
* | {{Lower back pain DDX}} | ||
==Evaluation== | |||
[[File:PchancefracX.png|thumb|Chance fracture of T10 and fracture of T9 due to a seatbelt during an MVC on xray.]] | |||
[[File:PchancefracCT.png|thumb|Chance fracture of T10 and fracture of T9 due to a seatbelt during an MVC on CT.]] | |||
===Workup=== | |||
*Obtain sagittally-reconstructed CT of thoracic and lumbar spines if suspect lap-belt mechanism or flexion-distraction | |||
**Evaluate for retropulsion of bony fragments | |||
*Obtain MRI to evaluate for ligamentous injuries or spinal cord injuries | |||
*Obtain CT chest/abdomen/pelvis if suspecting intra-abdominal injuries | |||
==Diagnosis== | ===Diagnosis=== | ||
* | *Pure bony injury from posterior to anterior through: | ||
* | **Spinous process | ||
**Pedicles | |||
**Vertebral body | |||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
*If no neurologic deficits present: | |||
**Non-operative immobilization with cast or TLSO | |||
*If neurologic deficits present: | |||
**Surgical decompression and fixation/fusion | |||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
*Admit | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations]] | |||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:Trauma]] | |||
[[Category:Neurology]] | |||
[[Category:Orthopedics]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:04, 18 October 2023
Background
- Unstable spinal fracture
- Extends horizontally posterior to anterior through the spinous process, pedicles, vertebral body
- Caused by flexion-distraction forces; ex. seatbelt use in MVC
- Upon deceleration, the spine forcibly flexes over the seatbelt, distracting (pulling apart) the middle/posterior column of spine
- Most common at T12-L2 due to spinal curvature and mechanism
- Incidence of concurrent intra-abdominal hollow viscus injuries is 50%[1]
- Ex. bowel perforations and mesenteric lacerations
- Intra-abdominal injuries more commonly associated than neuro deficits
- May be misdiagnosed as anterior compression fracture (usually stable)
Vertebral fractures and dislocations types
- Cervical fractures and dislocations
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
Clinical Features
- Back pain and thoracolumbar midline spinal tenderness to palpation
- Seatbelt sign: ecchymosis across the abdominal wall in the location of a lap belt[2]
- Abdominal pain
- Lower extremity neurological deficits
Differential Diagnosis
Lower Back Pain
- Spine related
- Acute ligamentous injury
- Acute muscle strain
- Disk herniation (Sciatica)
- Degenerative joint disease
- Spondylolithesis
- Epidural compression syndromes
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
- Cancer metastasis
- Spinal stenosis
- Transverse myelitis
- Vertebral osteomyelitis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Discitis
- Spinal Infarct
- Renal disease
- Intra-abdominal
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Ulcer perforation
- Retrocecal appendicitis
- Large bowel obstruction
- Pancreatitis
- Pelvic disease
- Other
Evaluation
Workup
- Obtain sagittally-reconstructed CT of thoracic and lumbar spines if suspect lap-belt mechanism or flexion-distraction
- Evaluate for retropulsion of bony fragments
- Obtain MRI to evaluate for ligamentous injuries or spinal cord injuries
- Obtain CT chest/abdomen/pelvis if suspecting intra-abdominal injuries
Diagnosis
- Pure bony injury from posterior to anterior through:
- Spinous process
- Pedicles
- Vertebral body
Management
- If no neurologic deficits present:
- Non-operative immobilization with cast or TLSO
- If neurologic deficits present:
- Surgical decompression and fixation/fusion
Disposition
- Admit
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Koay J, Davis DD, Hogg JP. Chance Fractures. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536926/
- ↑ Huecker MR, Chapman J. Seat Belt Injury. [Updated 2023 Apr 9]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470262/