Epidural hemorrhage: Difference between revisions
(→Workup) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
* Occur as a result of blood collecting between the skull and the dura mater | * Occur as a result of blood collecting between the skull and the dura mater | ||
* Most commonly secondary to a tear of the middle meningeal artery | |||
==Clinical Features== | |||
* Generally associated with blunt trauma to the temporal or temporoparietal region | * Generally associated with blunt trauma to the temporal or temporoparietal region | ||
* There is a high incidence of associated skull fractures (>75%) and additional cerebral injuries (intraparenchymal hemorrhage, cerebral contusion, contrecoup injuries, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage) | * There is a high incidence of associated skull fractures (>75%) and additional cerebral injuries (intraparenchymal hemorrhage, cerebral contusion, contrecoup injuries, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage) | ||
==Differential Diagnosis== | |||
{{Intracranial hemorrhage DDX}} | |||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 18: | ||
**Blood along the inside of the skull will not cross the sutures. This helps differentiate acute epidural hematoma from acute subdural hematoma. | **Blood along the inside of the skull will not cross the sutures. This helps differentiate acute epidural hematoma from acute subdural hematoma. | ||
==Workup== | ===Workup=== | ||
[[File:Epidural Hematoma.jpg|thumb|Epidural hematoma with biconvex shape hemorrhage.]] | [[File:Epidural Hematoma.jpg|thumb|Epidural hematoma with biconvex shape hemorrhage.]] | ||
{{Head trauma workup}} | {{Head trauma workup}} | ||
*Appropriate trauma resuscitation of all patients with head trauma | *Appropriate trauma resuscitation of all patients with head trauma | ||
*A thorough neurological examination of any patient with head trauma BEFORE administration of RSI | *A thorough neurological examination of any patient with head trauma BEFORE administration of RSI | ||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 35: | ||
*[[Intracranial Hemorrhage (Main)]] | *[[Intracranial Hemorrhage (Main)]] | ||
*[[Head Trauma]] | *[[Head Trauma]] | ||
*[[Epidural hematoma (spinal)]] | |||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
| Line 45: | Line 48: | ||
[[Category:Neuro]] | [[Category:Neuro]] | ||
[[Category:Trauma]] | [[Category:Trauma]] | ||
Revision as of 04:06, 7 April 2015
Background
- Occur as a result of blood collecting between the skull and the dura mater
- Most commonly secondary to a tear of the middle meningeal artery
Clinical Features
- Generally associated with blunt trauma to the temporal or temporoparietal region
- There is a high incidence of associated skull fractures (>75%) and additional cerebral injuries (intraparenchymal hemorrhage, cerebral contusion, contrecoup injuries, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage)
Differential Diagnosis
Intracranial Hemorrhage Types
- Intra-axial
- Hemorrhagic stroke (Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage)
- Traumatic intracerebral hemorrhage
- Extra-axial
- Epidural hemorrhage
- Subdural hemorrhage
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (aneurysmal intracranial hemorrhage)
Diagnosis
- Any patient with a neurologic deficit, depressed GCS, palpable skull fracture, or worrisome mechanism will warrant a non-contrast head CT after initial stabilization and resuscitation.
- Canadian CT Head Rule for patients with minor head injury
- Can be used to decide which minor injuries will require head CT
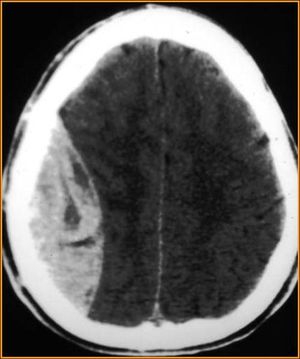
- Findings on CT are, classically, a lens (or lemon-shaped) shaped hyperdense lesion with sharp margins in the temporoparietal region
- Blood along the inside of the skull will not cross the sutures. This helps differentiate acute epidural hematoma from acute subdural hematoma.
Workup
Workup
- Consider head CT (rule out intracranial hemorrhage)
- Use validated decision rule to determine need
- Avoid CT in patients with minor head injury who are at low risk based on validated decision rules.[1]
- Consider cervical and/or facial CT
- Appropriate trauma resuscitation of all patients with head trauma
- A thorough neurological examination of any patient with head trauma BEFORE administration of RSI
Management
- Emergent neurosurgical evacuation
- Bilateral trephination (burr holes) if neurosurgery is unavailable
Disposition
- Transfer to tertiary medical center
- Admission to NS or Trauma Surgery
See Also
External Links
References
- Stiell IG, Wells GA, Vandemheen K, et al. The Canadian CT Head Rule for patients with minor head injury. Lancet. 2001;357(9266):1391-6.
- Judith E. Tintinalli, Gabor Kelen, J. Stephan Stapczynski. SAMJ. New York : McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division, c2004.; 2008.
- Irie F, Le Brocque R, Kenardy J et-al. Epidemiology of traumatic epidural hematoma in young age. J Trauma. 2011;71 (4): 847-53.