Hair tourniquet: Difference between revisions
Ostermayer (talk | contribs) (Text replacement - "Category:Peds" to "Category:Pediatrics") |
Neil.m.young (talk | contribs) (Text replacement - "==Diagnosis==" to "==Evaluation==") |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
*Crying infant | *Crying infant | ||
== | ==Evaluation== | ||
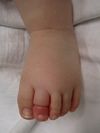
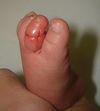
*Typically involves toes but can be located on fingers or genitals | *Typically involves toes but can be located on fingers or genitals | ||
*Constricting band with edema and/or redness distally | *Constricting band with edema and/or redness distally | ||
Revision as of 11:38, 23 July 2016
Background
- Also known as hair thread tourniquet syndrome
- Prompt diagnosis needed as ischemia can result
Clinical Features
- Crying infant
Evaluation
- Typically involves toes but can be located on fingers or genitals
- Constricting band with edema and/or redness distally
Management
- Simple removal with scissors
- Depilatory agent can be used if skin is intact (Nair)
- Apply for 8 minutes and rub agent and hair off
- Not effective on cotton or synthetic materials[1]
- Consider dorsal slit for cases where skin is broken and tourniquet is too tight for other methods
Disposition
- Discharge home
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Plesa JA, et al. Effect of a depilatory agent on cotton, polyester, and rayon versus human hair in a laboratory setting. Ann Emerg Med. 2015; 65(3):256-259.