Formal echocardiography: Difference between revisions
Ostermayer (talk | contribs) (Text replacement - " pts" to " patients") |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
**Below the line for pulmonic and aortic valves (systole) | **Below the line for pulmonic and aortic valves (systole) | ||
**Above the line in tricuspid and mitral valves (diastole) | **Above the line in tricuspid and mitral valves (diastole) | ||
===Parasternal long=== | |||
*Assess for mitral valve prolapse, systolic anterior motion | |||
*Differentiate pleural effusion from pericardial effusion | |||
**Pericardial effusion is anterior to descending aorta | |||
**Pleural effusion posterior to descending aorta | |||
[http://www.onlinejets.org/viewimage.asp?img=JEmergTraumaShock_2012_5_1_72_93118_u6.jpg Pericardial effusion vs. pleural effusion] | [http://www.onlinejets.org/viewimage.asp?img=JEmergTraumaShock_2012_5_1_72_93118_u6.jpg Pericardial effusion vs. pleural effusion] | ||
*Parasternal short | *EPSS, E-Point Septal Separation in PSL view | ||
**M-mode distance in mm between anterior leaflet of MV and septum in diastole | |||
**E-point is shortest distance | |||
**> 7 mm suggests severe systolic dysfunction | |||
**'''LVEF = 75.5 - 2.5 x EPSS''' in mm<ref>Silverstein JR et al. Quantitative Estimation of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction from Mitral Valve E-Point to Septal Separation and Comparison to Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Jan 2006. Vol 97, Issue 1, Pg 137=140.</ref> | |||
***EPSS and MRI LVEF correlated ~0.80 in study that generated equation | |||
***Excluded MV prostheses, asymmetrical septal hypertrophy, significant [[aortic regurgitation]] | |||
**Falsely elevated EPSS in: | |||
***[[Mitral stenosis]], rheumatic heart disease | |||
***Mitral calcification | |||
***[[Aortic regurgitation]] | |||
***LV dilation | |||
===Parasternal short=== | |||
===Apical=== | |||
*Best obtained in left lateral decubitus with L arm above head to open up ribs | |||
*EF estimation | |||
**LVEF by Simpson, LV volume change | **LVEF by Simpson, LV volume change | ||
**LVEF by Teichholz method, using M-mode (estimation of LV volume by diameter measured just beyond mitral tips in diastole) | **LVEF by Teichholz method, using M-mode (estimation of LV volume by diameter measured just beyond mitral tips in diastole) | ||
| Line 20: | Line 37: | ||
***30-44% = moderately depressed | ***30-44% = moderately depressed | ||
***<30% = severely depressed | ***<30% = severely depressed | ||
===Two chamber view=== | |||
===Three chamber view=== | |||
===Subxiphoid view=== | |||
===Suprasternal view=== | |||
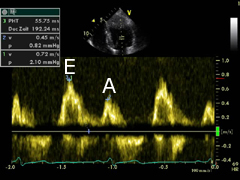
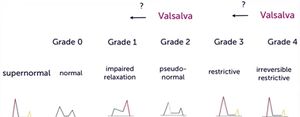
===E/A Ratio=== | ===E/A Ratio=== | ||
Revision as of 04:17, 7 July 2016
Diagnostic Pearls
- Normal directional flow in CW and PW in apical, parasternal short:
- Below the line for pulmonic and aortic valves (systole)
- Above the line in tricuspid and mitral valves (diastole)
Parasternal long
- Assess for mitral valve prolapse, systolic anterior motion
- Differentiate pleural effusion from pericardial effusion
- Pericardial effusion is anterior to descending aorta
- Pleural effusion posterior to descending aorta
Pericardial effusion vs. pleural effusion
- EPSS, E-Point Septal Separation in PSL view
- M-mode distance in mm between anterior leaflet of MV and septum in diastole
- E-point is shortest distance
- > 7 mm suggests severe systolic dysfunction
- LVEF = 75.5 - 2.5 x EPSS in mm[1]
- EPSS and MRI LVEF correlated ~0.80 in study that generated equation
- Excluded MV prostheses, asymmetrical septal hypertrophy, significant aortic regurgitation
- Falsely elevated EPSS in:
- Mitral stenosis, rheumatic heart disease
- Mitral calcification
- Aortic regurgitation
- LV dilation
Parasternal short
Apical
- Best obtained in left lateral decubitus with L arm above head to open up ribs
- EF estimation
- LVEF by Simpson, LV volume change
- LVEF by Teichholz method, using M-mode (estimation of LV volume by diameter measured just beyond mitral tips in diastole)
- EF visual assessment:
- >65% = hyperdynamic
- 55-65% = normal
- 45-54% = mildly depressed
- 30-44% = moderately depressed
- <30% = severely depressed
Two chamber view
Three chamber view
Subxiphoid view
Suprasternal view
E/A Ratio
- Measure of diastolic dysfunction
- PW doppler across MV in apical view
- The following rules will apply to most patients[2](Video)
- Rule 1: Normal diastolic function if echo normal, age<45 yrs, E>A
- Rule 2: Impaired relaxation if A>E, with E/A<1
- Rule 3: Pseudonormal if echo abnormal (LVH), age>65, E>A, E/A>1
- Rule 4: Restrictive filling if E/A>2
See Also
- Aortic stenosis for CW doppler measurements
External Links
References
- ↑ Silverstein JR et al. Quantitative Estimation of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction from Mitral Valve E-Point to Septal Separation and Comparison to Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Jan 2006. Vol 97, Issue 1, Pg 137=140.
- ↑ 123sonography. Nov 20, 2010. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qdLkbcFe_DI.