Foot and toe fractures: Difference between revisions
Mceledon83 (talk | contribs) |
Mceledon83 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
**1. Tuberosity (styloid) avulsion fracture | **1. Tuberosity (styloid) avulsion fracture | ||
***Most common fx at base of 5th metatarsal | ***Most common fx at base of 5th metatarsal | ||
***Sx often mild, | ***Sx often mild, pts usually present with sprained ankle complaint | ||
***Occurs due to forced inversion foot/ankle while in plantar flexion | ***Occurs due to forced inversion foot/ankle while in plantar flexion | ||
**2. Jones or metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction fracture | **2. Jones or metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction fracture | ||
Revision as of 03:59, 22 August 2013
Hindfoot
Talus
Background
- Almost always associated with other injuries
Diagnosis
- CT often required for accurate diagnosis
Management
- Major fracture (talar neck and head)
- Immediate ortho consultation required (high rate of avascular necrosis)
- Minor fracture
- Posterior splint, NWB, ortho referral
Calcaneus
Background
- Associated injuries are common
- Types
- Intra-articular (75%)
- Sclerotic line may be only evidence of impacted fracture
- Extra-articular (25%)
- Anterior process fx is most common
- Intra-articular (75%)
Diagnosis
- Imaging
- Decreased Boehler's angle (<25') may be only sign of fx (compare w/ opposite side)
Treatment
- Intra-articular fracture
- Immobilization w/ posterior splint
- Non-weightbearing
- Elevation (very important - fx has high rate of severe swelling)
- Ortho consult
- Extra-articular fracture
- Immobilization and close ortho f/u
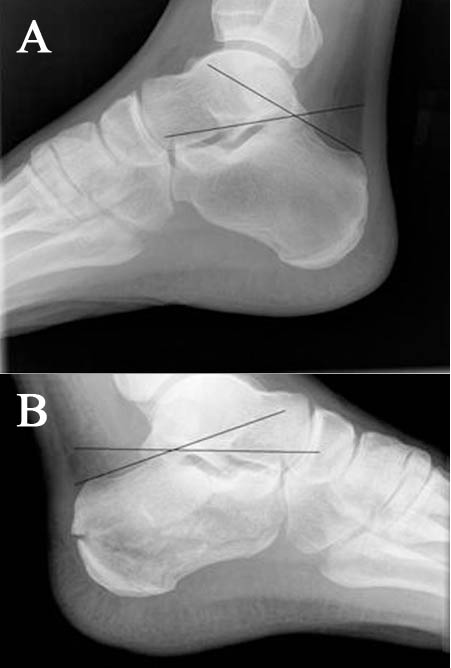
Images
- (A) Normal Boehler's angle and (B) Abnormal Boehler's angle
Midfoot
LisFranc Injury
- See Lisfranc Injury
- All are diagnosed/managed in similar way
- Imaging: (weight-bearing AP, lateral, oblique)
- CT sometimes necessary
- Treatment: Non-weightbearing short leg cast, ortho referral
- Imaging: (weight-bearing AP, lateral, oblique)
Forefoot
Fifth Metatarsal
Background
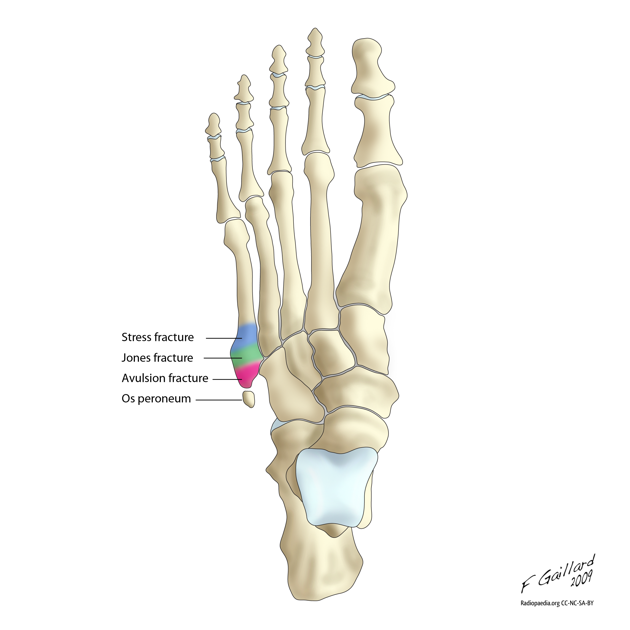
- 3 types of fractures:
- 1. Tuberosity (styloid) avulsion fracture
- Most common fx at base of 5th metatarsal
- Sx often mild, pts usually present with sprained ankle complaint
- Occurs due to forced inversion foot/ankle while in plantar flexion
- 2. Jones or metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction fracture
- Occurs due to sudden change in direction w/ heel off the ground
- 3. Diaphyseal stress fracture
- Occurs through repetitive microtrauma
- 1. Tuberosity (styloid) avulsion fracture
Diagnosis
- Plain radiographs are usually adequate
Management
- Tuberosity Fracture
- Walking cast and weightbearing as tolerated
- Jones Fracture (non-displaced)
- Posterior splinting, NWB, ortho referral
- Diaphyseal Stress Fracture
- Ortho referral
Metatarsal
Background
- Must rule-out associated Lisfranc injury
Management
- Posterior splint, NWB, ortho referral in 2-3d
Phalange
- Management: buddy-taping, hard-soled shoe
See Also
Source
- Tintinalli
- Ilustration by Dr. Frank Gaillard; CC SA NC BY licence
- http://radiopaedia.org/articles/jones_fracture