Thoracic and lumbar compression fractures: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
*Nonoperative:orthosis, calcitonin, biphophanates. | |||
*kyphoplasty | |||
*vertebroplasty | |||
*surgical decompression and stabilization | |||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
Home if fracture stable and pain control optimal. | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:45, 27 January 2021
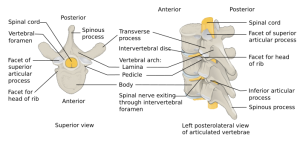
Background
- Also known as a "wedge fracture"
- Only unstable if posterior ligament complex ruptures (requires a rotational force)
- Unlikely to cause cord damage
Vertebral fractures and dislocations types
- Cervical fractures and dislocations
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
Clinical Features
- Mechanism: axial loading and flexion
Differential Diagnosis
Thoracic Trauma
- Airway/Pulmonary
- Cardiac/Vascular
- Musculoskeletal
- Other
Lower Back Pain
- Spine related
- Acute ligamentous injury
- Acute muscle strain
- Disk herniation (Sciatica)
- Degenerative joint disease
- Spondylolithesis
- Epidural compression syndromes
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
- Cancer metastasis
- Spinal stenosis
- Transverse myelitis
- Vertebral osteomyelitis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Discitis
- Spinal Infarct
- Renal disease
- Intra-abdominal
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Ulcer perforation
- Retrocecal appendicitis
- Large bowel obstruction
- Pancreatitis
- Pelvic disease
- Other
Evaluation
Workup
Diagnosis
- Suspect instability and obtain CT if:
- Severe compression (>50% loss of vertebral height)
- Kyphosis >30deg
- Rotational component to injury
- Compression fracture at multiple sites
- Posterior cortex abnormality
Management
- Nonoperative:orthosis, calcitonin, biphophanates.
- kyphoplasty
- vertebroplasty
- surgical decompression and stabilization
Disposition
Home if fracture stable and pain control optimal.