Arthrocentesis: Difference between revisions
Gatordoc77 (talk | contribs) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Indications == | == Indications == | ||
*Suspicion of septic arthritis | |||
*Suspicion of crystal induced arthritis | |||
*Evaluation of therapeutic response for septic arthritis | |||
* | *Unexplained arthritis with synovial effusion | ||
* | |||
* | |||
=== Relative Indications === | === Relative Indications === | ||
*Therapeutic (decrease intra-articular pressure, injection of anesthetics/steroids) | |||
Therapeutic (decrease intra-articular pressure, injection of anesthetics/steroids) | |||
== Contraindications == | == Contraindications == | ||
#No absolute contraindications for diagnostic arthrocentesis | #No absolute contraindications for diagnostic arthrocentesis | ||
# | #Do not inject steroids into a joint that you suspect is already infected | ||
#Relative Contraindications: | #Relative Contraindications: | ||
## | ##Overlying cellulitis | ||
## | ##Coagulopathy | ||
##Joint prosthesis (refer to ortho) | ##Joint prosthesis (refer to ortho) | ||
== Equipment Needed == | == Equipment Needed == | ||
#Betadine or Chlorhexadine | #Betadine or Chlorhexadine | ||
#Sterile | #Sterile gloves/drape | ||
# | #Sterile gauze | ||
#Lidocaine | #Lidocaine | ||
#Syringes | #Syringes | ||
## | ##Small syringe (6-12cc) for injection of local anesthetic | ||
##Large (one 60cc or | ##Large syringe (one 60cc or two 30cc) for aspiration | ||
#Needles | #Needles | ||
##18 | ##18 gauge | ||
##27 gauge | ##27 gauge | ||
#Collection tubes (red | #Collection tubes (red top) | ||
#Culture bottles | #Culture bottles | ||
== Procedure == | == Procedure == | ||
#Prep area w/ betadine or chlorhexadine using circular motion moving away from joint x 3 | |||
#Drape joint in sterile fashion | |||
#Prep | #Inject lidocaine w/ 25-30ga needle superficially and then into deeper tissues | ||
#Inject lidocaine superficially and then into | #Insert 18ga needle (for larger joints) into joint space while pulling back on syringe #Stop once you aspirate fluid; aspirate as much fluid as possible | ||
# | ##Send: cell count, culture, Gram stain, crystal analysis | ||
# | |||
== Approach == | == Approach == | ||
=== Shoulder === | === Shoulder === | ||
#Anterior approach | |||
# | ##Sit pt upright facing you | ||
# | ##Insert needle just lateral to coracoid process (between coracoid process and humeral head) | ||
##Direct needle posteriorly | |||
#Posterior Approach | |||
##Sit pt upright w/ back facing you | |||
##Palpate scapular spine to its lateral limit (the acromion) | |||
##Identify the posterolateral corner of the acromion | |||
##Insert 1.5in needle 1 cm inferior and 1 cm medial to this corner | |||
##Direct needle anterior and medial toward presumed position of coracoid process | |||
##Glenohumeral joint is located at a depth of approximately 1-1.5in | |||
=== Elbow === | === Elbow === | ||
#Place elbow in 90' flexion, resting on a table, w/ hand prone | |||
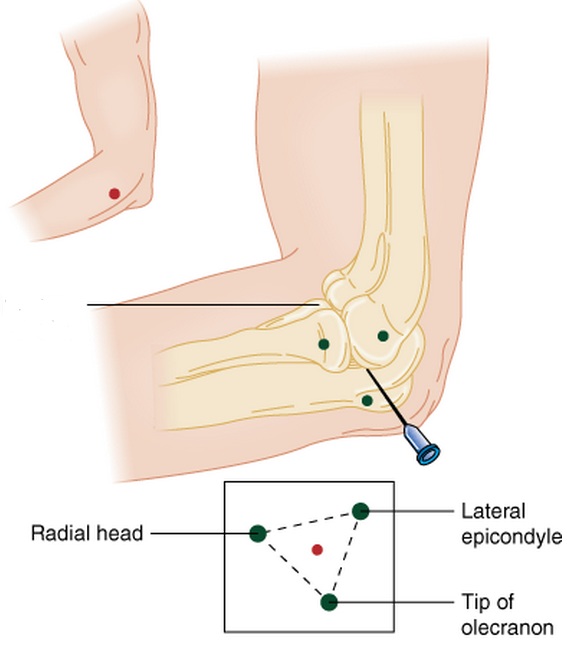
# | #Locate radial head, lateral epicondyle , and lateral aspect of olecranon tip | ||
# | ##These landmarks form the anconeus triangle | ||
#Palpate a sulcus just proximal to the radial head (in the middle of the triangle) | |||
#Insert needle into sulcus directed medial and perpendicular to radius toward distal end of antecubital fossa | |||
[[File:Shoulder Arthrocentesis.jpg]] | |||
=== Wrist === | === Wrist === | ||
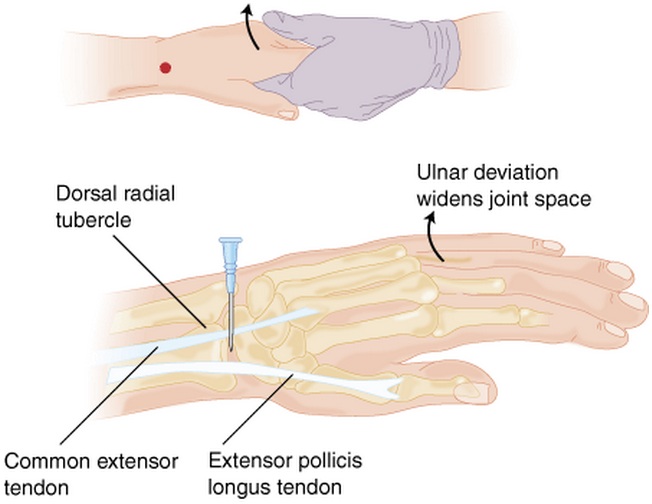
#Palpate landmarks w/ wrist in neutral position: | |||
##Radial tubercle of distal radius | |||
##Anatomic snuffbox | |||
##Extensor pollicis longus tendon | |||
##Common extensor tendon of index finger | |||
#Insert needle perpendicular to skin, ulnar to radial tubercle and anatomic snuffbox, between extensor pollicis longus and common extensor tendons | |||
[[File:Wrist Arthrocentesis.jpg]] | |||
# | === Knee === | ||
#Can be entered medially or laterally to the patella | |||
#Fully extend knee and ensure quadriceps muscle is relaxed | |||
#Identify midpoint of patella; insert needle either lateral or medial | |||
#Direct needle posterior to patella and horizontally toward the joint space | |||
#Compression or "milking" applied to both sides of joint space may facilitate aspiration | |||
=== Ankle === | |||
#Lateral approach (subtalar) | |||
##Keep foot perpendicular to leg | |||
##Enter subtalar joint just below tip of lateral malleolus | |||
##Direct needle medially toward joint space | |||
#Medial approach (tibiotalar) | |||
##Have pt supine w/ foot perpendicular to leg | |||
##Palpate sulcus lateral to medial malleolus and medial to TA and EHL tendons | |||
##Then plantarflex foot w/ needle entering skin overlying the sulcus | |||
##Angle needle slightly cephalad as it passes between medial malleolus and TA tendon | |||
=== Metacarpophalangeal === | === Metacarpophalangeal === | ||
#have palm facing down and apply gentle traction to the affected digit | #have palm facing down and apply gentle traction to the affected digit | ||
#insert needle dorsally just medial or lateral to midline and proximal to the base of the proximal phalanx | #insert needle dorsally just medial or lateral to midline and proximal to the base of the proximal phalanx | ||
=== Interphalangeal === | === Interphalangeal === | ||
#have palm facing down and apply gentle traction to the affected digit | #have palm facing down and apply gentle traction to the affected digit | ||
#insert needle dorsally medial or lateral to midline and proximal to base of middle or distal phalanx | #insert needle dorsally medial or lateral to midline and proximal to base of middle or distal phalanx | ||
=== Metatarsophalangeal === | === Metatarsophalangeal === | ||
| Line 108: | Line 122: | ||
== Source == | == Source == | ||
*Tintinalli | |||
http://emprocedures.com/arthrocentesis/introduction.htm | *http://emprocedures.com/arthrocentesis/introduction.htm | ||
[[Category:Procedures]] [[Category:Ortho]] | [[Category:Procedures]] [[Category:Ortho]] | ||
Revision as of 20:09, 27 February 2012
Indications
- Suspicion of septic arthritis
- Suspicion of crystal induced arthritis
- Evaluation of therapeutic response for septic arthritis
- Unexplained arthritis with synovial effusion
Relative Indications
- Therapeutic (decrease intra-articular pressure, injection of anesthetics/steroids)
Contraindications
- No absolute contraindications for diagnostic arthrocentesis
- Do not inject steroids into a joint that you suspect is already infected
- Relative Contraindications:
- Overlying cellulitis
- Coagulopathy
- Joint prosthesis (refer to ortho)
Equipment Needed
- Betadine or Chlorhexadine
- Sterile gloves/drape
- Sterile gauze
- Lidocaine
- Syringes
- Small syringe (6-12cc) for injection of local anesthetic
- Large syringe (one 60cc or two 30cc) for aspiration
- Needles
- 18 gauge
- 27 gauge
- Collection tubes (red top)
- Culture bottles
Procedure
- Prep area w/ betadine or chlorhexadine using circular motion moving away from joint x 3
- Drape joint in sterile fashion
- Inject lidocaine w/ 25-30ga needle superficially and then into deeper tissues
- Insert 18ga needle (for larger joints) into joint space while pulling back on syringe #Stop once you aspirate fluid; aspirate as much fluid as possible
- Send: cell count, culture, Gram stain, crystal analysis
Approach
Shoulder
- Anterior approach
- Sit pt upright facing you
- Insert needle just lateral to coracoid process (between coracoid process and humeral head)
- Direct needle posteriorly
- Posterior Approach
- Sit pt upright w/ back facing you
- Palpate scapular spine to its lateral limit (the acromion)
- Identify the posterolateral corner of the acromion
- Insert 1.5in needle 1 cm inferior and 1 cm medial to this corner
- Direct needle anterior and medial toward presumed position of coracoid process
- Glenohumeral joint is located at a depth of approximately 1-1.5in
Elbow
- Place elbow in 90' flexion, resting on a table, w/ hand prone
- Locate radial head, lateral epicondyle , and lateral aspect of olecranon tip
- These landmarks form the anconeus triangle
- Palpate a sulcus just proximal to the radial head (in the middle of the triangle)
- Insert needle into sulcus directed medial and perpendicular to radius toward distal end of antecubital fossa
Wrist
- Palpate landmarks w/ wrist in neutral position:
- Radial tubercle of distal radius
- Anatomic snuffbox
- Extensor pollicis longus tendon
- Common extensor tendon of index finger
- Insert needle perpendicular to skin, ulnar to radial tubercle and anatomic snuffbox, between extensor pollicis longus and common extensor tendons
Knee
- Can be entered medially or laterally to the patella
- Fully extend knee and ensure quadriceps muscle is relaxed
- Identify midpoint of patella; insert needle either lateral or medial
- Direct needle posterior to patella and horizontally toward the joint space
- Compression or "milking" applied to both sides of joint space may facilitate aspiration
Ankle
- Lateral approach (subtalar)
- Keep foot perpendicular to leg
- Enter subtalar joint just below tip of lateral malleolus
- Direct needle medially toward joint space
- Medial approach (tibiotalar)
- Have pt supine w/ foot perpendicular to leg
- Palpate sulcus lateral to medial malleolus and medial to TA and EHL tendons
- Then plantarflex foot w/ needle entering skin overlying the sulcus
- Angle needle slightly cephalad as it passes between medial malleolus and TA tendon
Metacarpophalangeal
- have palm facing down and apply gentle traction to the affected digit
- insert needle dorsally just medial or lateral to midline and proximal to the base of the proximal phalanx
Interphalangeal
- have palm facing down and apply gentle traction to the affected digit
- insert needle dorsally medial or lateral to midline and proximal to base of middle or distal phalanx
Metatarsophalangeal
- patient supine with flexion of the MTP joint 15-20 degrees and apply gentle traction
- insert needle dorsally just medial or lateral to midline between the metatarsal head and base of proximal phalanx
Interphalangeal
- patient supine with joint flexed 15-20 degrees with gentle traction
- insert needle dorsally, medial or lateral to midline between head of proximal phalanx and base of more distal phalanx
Complications
- pain
- infection
- reaccumulation of effusion
- damage to tendons, nerves, or blood vessels