Dysphonia: Difference between revisions
Neil.m.young (talk | contribs) (Text replacement - "==Sources==" to "==References==") |
(Added a background section) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
[[File:Dysphonia.png|thumb|Dysphonia Algorithm]] | [[File:Dysphonia.png|thumb|Dysphonia Algorithm]] | ||
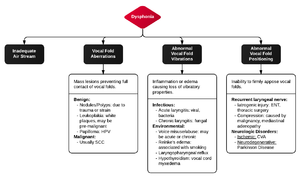
Dysphonia, otherwise known as voice hoarseness, is any problem related to speaking or phonation. This can be caused by myriad of disease processes affecting air stream into the larynx, or vocal cord vibrations. Dysphonia can resent as a variety of complaints, including shortness of breath, vocal tremor, altered pitch, or complete loss of voice. The table below illustrates the 4 main pathophysiologic modalities by which dysphonia is thought to occur. | |||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
Revision as of 18:45, 5 September 2016
Background
Dysphonia, otherwise known as voice hoarseness, is any problem related to speaking or phonation. This can be caused by myriad of disease processes affecting air stream into the larynx, or vocal cord vibrations. Dysphonia can resent as a variety of complaints, including shortness of breath, vocal tremor, altered pitch, or complete loss of voice. The table below illustrates the 4 main pathophysiologic modalities by which dysphonia is thought to occur.