Pelvic avulsion fracture: Difference between revisions
ClaireLewis (talk | contribs) |
ClaireLewis (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
*Trauma may be very minor (e.g. fall from seated) in elderly or those with weakened bones | *Trauma may be very minor (e.g. fall from seated) in elderly or those with weakened bones | ||
*Sports-related avulsion fractures are most common pelvic injuries in children | *Sports-related avulsion fractures are most common pelvic injuries in children | ||
[[File:PelvicAvulsionFx.png|thumb|Avulsion fracture of: (1) Iliac wing (Duverney fracture) (2) Superior pubic ramus (3) Inferior pubic ramus (4) Transverse sacral (5) Coccyx fracture. (6) Anterior superior iliac spine (7) Anterior inferior iliac spine (8) Ischial tuberosity] | |||
] | |||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
*History of trauma | *History of trauma | ||
Revision as of 19:32, 5 September 2016
Background
- Isolated, closed avulsion fracture of pelvis or single-bone
- Trauma may be very minor (e.g. fall from seated) in elderly or those with weakened bones
- Sports-related avulsion fractures are most common pelvic injuries in children
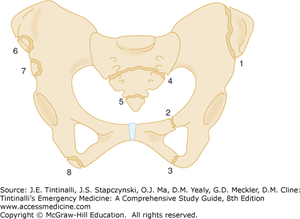
Avulsion fracture of: (1) Iliac wing (Duverney fracture) (2) Superior pubic ramus (3) Inferior pubic ramus (4) Transverse sacral (5) Coccyx fracture. (6) Anterior superior iliac spine (7) Anterior inferior iliac spine (8) Ischial tuberosity] ]


