Dental abscess
Background
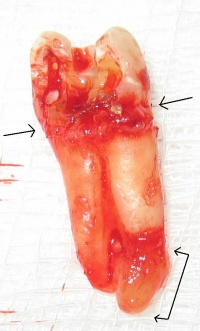
Tooth #4, the maxillary right second premolar, after extraction. The two single-headed arrows point to the CEJ, which is the line separating the crown (in this case, heavily decayed) and the roots. The double headed arrow (bottom right) shows the extent of the abscess that surrounds the apex of the palatal root.
- Associated with dental caries or nonviable teeth
- Significant erosion of the pulp with bacterial overgrowth
Clinical Features
- Acute pain, swelling, and mild tooth elevation
- Exquisite sensitivity to percussion or chewing on the involved tooth
- Swelling in surrounding gingiva, buccal, lingual or palatal regions
- May see small white pustule (parulis) in gingival surface characteristic for abscesses
Differential Diagnosis
Dentoalveolar Injuries
Odontogenic Infections
- Acute alveolar osteitis (dry socket)
- Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (trench mouth)
- Dental abscess
- Periapical abscess
- Periodontal abscess
- Ludwig's angina
- Pulpitis (dental caries)
- Pericoronitis
- Peritonsillar abscess (PTA)
- Retropharyngeal abscess
- Vincent's angina - tonsillitis and pharyngitis
Other
Evaluation
- Clinical evaluation
- Radiographs
Management
- Analgesia with NSAIDs, opiates and local anesthetics
- Dental follow-up within 48 hrs.
- Emergent oral surgeon followup if complicated (Ludwig's angina, Lemierre's syndrome)
Antibiotics
Treatment is broad and focused on polymicrobial infection
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate 875 mg PO q12 hours x 7-14 days
- Clindamycin 450 mg PO q8 hours x 7-14 days
- Penicillin VK 500 mg PO q6 hours x 7-14 days (frequently prescribed but no longer recommended as monotherapy)
- Ampicillin/Sulbactam 3g IV q6 hours x 7 days
I&D
- Can be performed in ED depending on provider comfort or by a dental consultant
Procedure
- 11 or 12 blade stab incision
- Hemostat blunt dissection +/- packing
See Also
References
- ER Atlas





