Scarlet fever
Background
- Caused by Group A Strep
Clinical Features
- Prodrome of fever, sore throat, vomiting, abdominal pain followed by rash 1-2d later
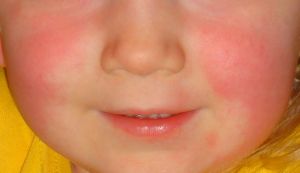
- Rash
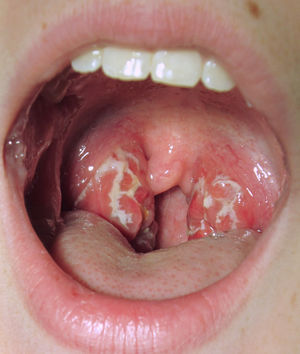
- Enanthem (rash involving mucous membrane)
- Tonsils/pharynx are red and covered with exudate
- Tongue may have initial exudate followed by erythema ("strawberry tongue)
- Soft palate have bright-red spots
- Exanthem
- Begins 1-2days after onset of illness
- Starts on neck, axillae, groin, spreads to trunk and extremities
- Red, finely punctate, sandpaper feel
- Pastia lines: linear petechial eruptions in antecubital/axilla
- Desquamation follows
- Enanthem (rash involving mucous membrane)
Differential Diagnosis
Pediatric Rash
- Atopic dermatitis
- Bed bugs
- Contact dermatitis
- Drug rash
- Erythema infectiosum (Fifth disease)
- Hand-foot-and-mouth disease
- Henoch-schonlein purpura (HSP)
- Herpangina
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Meningitis
- Measles
- Molluscum contagiosum
- Roseola infantum
- Rubella (German measles)
- Scabies
- Scarlet fever
- Smallpox
- Varicella (Chickenpox)
Erythematous rash
- Positive Nikolsky’s sign
- Febrile
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (children)
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis/SJS (adults)
- Afebrile
- Febrile
- Negative Nikolsky’s sign
- Febrile
- Afebrile
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis, based on history and physical exam
Management
- Treatment (to reduce rheumatic fever / nephritis)
- Penicillin VK 50mg/kg BID x 10d OR Amoxicillin 50mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses or one time dose x10d[1]
- If allergic to penicillin → Azithromycin 10mg/kg on day 1, 5mg/g days 2-5
Disposition
- Discharge