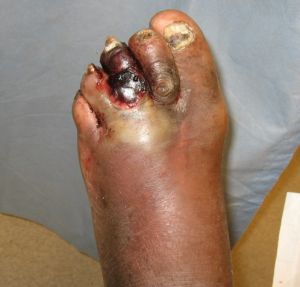
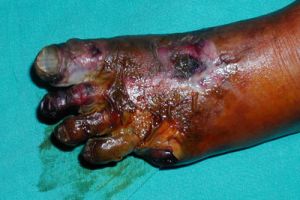
Wet gangrene
Background
Gangrene General Info
- A form of tissue necrosis characterized by critically insufficient blood supply leading to tissue death.
- Primarily divided into wet gangrene vs dry gangrene. Other, specific forms of gangrene include Fournier's gangrene, gas gangrene, and necrotizing fasciitis.
- Most commonly occur in distal extremities, clasically the feet.
- Main risk factors are diabetes, smoking, and peripheral arterial disease.
Clinical Features
- Usually due to peripheral arterial or venous disease, but can also be sequelae of trauma or burns causing vascular injuries.
- Presents with swollen, pale, soft tissue, often with a putrid smell and purulent discharge.
- As tissue is infected, wet gangrene presents a higher risk of systemic infection than dry gangrene.
Differential Diagnosis
Foot infection
- Gout
- PsuedoGout
- Cellulitis
- Gangrene
- Trench foot
- Abscess
- Necrotizing soft tissue infections
- Osteomyelitis
- Diabetic foot infection
- Charcot Foot
Look A-Likes
Evaluation
Workup
- CBC
- Chemistry
- Consider:
- X-ray
- blood cultures
- lactate
Diagnosis
- History and physical examination are usually sufficient to make the diagnosis.
- Given higher risk for systemic infection, patients should be evaluated for signs/symptoms of sepsis
Management
- Requires surgical consultation as rapid debridement or amputation of necrotic tissue is required to prevent further spread of infection.
Antibiotics
Initial use broad spectrum antibiotic coverage, as these are often polymycrobial infections.
- Example 1:
- Cefepime 1g IV q24h [infuse first] +
- Metronidazole 500mg IV q8h +
- Vancomycin 1g IV (or per pharmacy) +
- Consider additionally: clindamycin 900mg IV q8h (if suspect anerobic/gas gangrene/streptococcal toxic shock syndrome)
- Example 2 (possible substitutions):
- Substitute piperacillin-tazobactam OR meropenem for broad-spectrum coverage
- Substitute linezolid for MRSA coverage
- Substitute penicillin G for anaerobic coverage.
Disposition
- Admission