ECG Basics: Difference between revisions
Mceledon83 (talk | contribs) (→RAE) |
Mceledon83 (talk | contribs) (→RAE) |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
*Right atrial hyper.-initial component is larger in V1 than V6 | *Right atrial hyper.-initial component is larger in V1 than V6 | ||
#p-mitrale-m notched p wave in leads 1 and 2. Greater than .12 seconds. | #p-mitrale-m notched p wave in leads 1 and 2. Greater than .12 seconds. | ||
[[File:RAE.png|thumb|RAE]] | [[File:RAE.png|thumb|left|100px||RAE]] | ||
== LAE == | == LAE == | ||
Revision as of 00:07, 20 August 2013
General
- 1 small box = 1mm = 0.04 sec = 40 miliseconds
- 5 small boxes = 1 big box = 5mm = 0.2 sec = 200 miliseconds
- Entire ECG strip is ~10 seconds
Intervals
| Interval | Time (s) | Boxes |
| PR | 0.12 - 0.20 | 3-5 |
| QRS | .06 - 0.10 | 1.5-2.5 |
| QTc | <0.44 | N/A |
Axis
- Cannot be measured if BBBs are present
- If up in leads 1 and AVF then normal axis
Q waves
- Significant if >1 box wide or if is 1/3 of entire QRS amplitude
- Early Repolarization:
- ST elevation most prominent in lat precord leads (V4-6) but no reciprocal changs
- T waves usually broad, tall (>5mm) & upright
- Limb leads may also have ST elevation, rarely >2 mm
T waves
- Normally upright in 1, 2, V3-V6
- Negative in AVR
- If is greater than 2/3 height of R wave then is abnormal
- Deep symmetrical inverted T waves:
- Left ventricle apical hypertrophy
- Raised ICP (e.g.SAH)
- Wellen's (MI)
- Paced rhythm
- BBB's or WPW
- Idiopathic
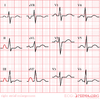
RAE
- Rarely isolated finding (usually RVH/RAD also)
- P amplitude >2.5mm in II
- Large biphasic p wave in V1
- Right atrial hyper.-initial component is larger in V1 than V6
- p-mitrale-m notched p wave in leads 1 and 2. Greater than .12 seconds.
LAE
- Biphasic P in V1 w/ wide, deep terminal component, >1mm depth & wide
- Left atrial hyper.-terminal component is larger than .04 sec.
LVH
- Sum of S in V1 or V2 & R in V5 or V6 is >35mm
- Sum of highest R & deepest S in precord is >45mm
- R wave in V6 > 18mm
- R in AVL of >12mm
- L precordial leads may show ST depression & TWI = LV strain pattern
- LAD-with slightly wide QRS. Or r in avl greater than 11mm, r in 1 is greater than 12mm, or R in AVf is greater than 20mm
RVH
- Dominant R in V1 >7mm (also seen in WPW, RBBB, post MI, & nml var)
- RSR in V1 w/ QRS < 0.12
- This dx usu also w/ RAE or strain (ST dep w/ twi in V1-V3).
- Less sens. & spec. than LVH, usu nl ecg
- RVH-R wave greater than S in V1, but gets progressively smaller from V1 to V6. S wave persists in V5 and V6. RAD with slightly wide QRS.
- (note: R :S ratio greater than 1 also in: 1.RBBB 2.WPW type A. 3. Post. Wall MI. 4.kids.)
RBBB
- QRS > 0.12 in limb leads
- Triphasic QRS (rSR'), often w/ ST depression & TWI in V1-V3
- V1 must have a positive complex
- Slurred S in 1 and V6
LBBB
- ST depression and TWI are common
- QRS > 0.12 in limb leads
- Leads
- Large and wide R waves — leads I, aVL, V5, and V6
- Small R wave followed by deep S wave —leads II, III, aVF, V1–V3
LAFB
- Left axis deviation (-45 or more) w/QRS <0.10s
- Deep S in II, III, and AVF
LPFB
- Usually means disease
- Right axis deviation (>110) w/QRS < 0.10s
- Tall R in II, III, AVF
- Exclude other causes (COPD, RVH, Lat MI)
Source
9/09 DONALDSON (adapted from Niemann, Lampe, Pani)
Journal of Electrocardiology. Vol 43 (2010). 40-42.