CO2 narcosis: Difference between revisions
Neil.m.young (talk | contribs) (Text replacement - "==Diagnosis==" to "==Evaluation==") |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
*Increased CO2 in the blood leading to depressed mental status | [[File:Respiratory system complete en.svg|thumb|]] | ||
*Most commonly seen in acute exacerbations of obstructive pulmonary diseases | [[File:Gas exchange.jpg|thumb|Normal gas exchange showing compositions of the ambient air, the alveolar air (light blue) with which the alveolar capillary blood equilibrates, and the blood gas tensions in the pulmonary arterial (blue blood entering the lung on the left) and venous blood (red blood leaving the lung on the right). All the gas tensions are in kPa (to convert to mm Hg, multiply by 7.5).]] | ||
*[[hypercapnia|Increased CO2]] in the blood leading to depressed mental status | |||
*Most commonly seen in acute exacerbations of obstructive pulmonary diseases (e.g. [[COPD]], [[asthma]]) | |||
*Can also be seen in [[Scuba diving emergencies|SCUBA divers]] | *Can also be seen in [[Scuba diving emergencies|SCUBA divers]] | ||
| Line 7: | Line 9: | ||
*[[Headache]] | *[[Headache]] | ||
*[[Confusion]] | *[[Confusion]] | ||
*Lethargy | *[[Lethargy]] | ||
*Propensity for [[arrhythmias]] | *Propensity for [[arrhythmias]] | ||
*[[Seizure]] | *[[Seizure]] | ||
| Line 16: | Line 18: | ||
==Evaluation== | ==Evaluation== | ||
*VBG (ABG not required to make this diagnosis<ref>McCanny P, Bennett K, Staunton P, McMahon G. Venous vs arterial blood gases in the assessment of patients presenting with an exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Emerg Med. 2012; 30(6):896-900.</ref>) | *[[VBG]] (ABG not required to make this diagnosis<ref>McCanny P, Bennett K, Staunton P, McMahon G. Venous vs arterial blood gases in the assessment of patients presenting with an exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Emerg Med. 2012; 30(6):896-900.</ref>) | ||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
*Hyperventilation with either NIPPV or intubation/mechanical ventilation depending on severity and patient's mental status | *Hyperventilation with either [[biPAP|NIPPV]] or [[intubation]]/mechanical ventilation depending on severity and patient's mental status | ||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
Latest revision as of 22:22, 1 May 2024
Background
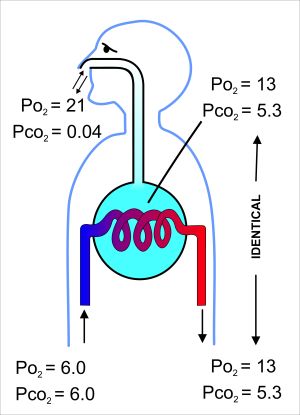
Normal gas exchange showing compositions of the ambient air, the alveolar air (light blue) with which the alveolar capillary blood equilibrates, and the blood gas tensions in the pulmonary arterial (blue blood entering the lung on the left) and venous blood (red blood leaving the lung on the right). All the gas tensions are in kPa (to convert to mm Hg, multiply by 7.5).
- Increased CO2 in the blood leading to depressed mental status
- Most commonly seen in acute exacerbations of obstructive pulmonary diseases (e.g. COPD, asthma)
- Can also be seen in SCUBA divers
Clinical Features
Differential Diagnosis
Altered mental status
Diffuse brain dysfunction
- Hypoxic encephalopathy
- Acute toxic-metabolic encephalopathy (Delirium)
- Hypoglycemia
- Hyperosmolar state (e.g., hyperglycemia)
- Electrolyte Abnormalities (hypernatremia or hyponatremia, hypercalcemia)
- Organ system failure
- Hepatic Encephalopathy
- Uremia/Renal Failure
- Endocrine (Addison's disease, Cushing syndrome, hypothyroidism, myxedema coma, thyroid storm)
- Hypoxia
- CO2 narcosis
- Hypertensive Encephalopathy
- Toxins
- TTP / Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Alcohol withdrawal
- Drug reactions (NMS, Serotonin Syndrome)
- Environmental causes
- Deficiency state
- Wernicke encephalopathy
- Subacute Combined Degeneration of Spinal Cord (B12 deficiency)
- Vitamin D Deficiency
- Zinc Deficiency
- Sepsis
- Osmotic demyelination syndrome (central pontine myelinolysis)
- Limbic encephalitis
Primary CNS disease or trauma
- Direct CNS trauma
- Diffuse axonal injury
- Subdural/epidural hematoma
- Vascular disease
- SAH
- Stroke
- Hemispheric, brainstem
- CNS infections
- Neoplasms
- Paraneoplastic Limbic encephalitis
- Malignant Meningitis
- Pancreatic Insulinoma
- Seizures
- Nonconvulsive status epilepticus
- Postictal state
- Dementia
Psychiatric
Evaluation
Management
- Hyperventilation with either NIPPV or intubation/mechanical ventilation depending on severity and patient's mental status
Disposition
- Admission to a monitored setting
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ McCanny P, Bennett K, Staunton P, McMahon G. Venous vs arterial blood gases in the assessment of patients presenting with an exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Emerg Med. 2012; 30(6):896-900.