Neonatal seborrhoeic dermatitis: Difference between revisions
Ostermayer (talk | contribs) (Text replacement - "Category:Peds" to "Category:Pediatrics") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
*Clinical diagnosis | *Clinical diagnosis | ||
**Consider immunosuppression or [[HIV]] in severe or widespread lesions | |||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
*Application of mineral oil followed by washing and removal of scales with comb | *Application of mineral oil followed by washing and removal of scales with comb | ||
*Avoid topical steroids | *Avoid topical steroids | ||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
Revision as of 10:54, 11 May 2016
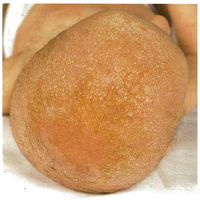
Background
- Also known as cradle cap, infantile seborrhoeic dermatitis, crusta lactea, milk crust, and honeycomb disease
- Starts between 2-6wk of life; improves by 6 months
- Malassezia furfur, non-contagious fungus
Clinical Features
- Greasy yellow-red scales
- Proclivity for scalp (cradlecap), but may find around ears, cheeks, neck
- Not pruritic
- Also axilla and groin where there are significant sebaceous glands
Differential Diagnosis
Neonatal Rashes
- Acne
- Atopic dermatitis
- Candidiasis
- Contact dermatitis
- Diaper dermatitis
- Erythema toxicum neonatorum
- Impetigo
- Mastitis
- Milia
- Miliaria
- Mongolian spots
- Omphalitis
- Perianal streptococcal dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Pustular melanosis
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Sucking blisters
- Tinea capitis
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis
- Consider immunosuppression or HIV in severe or widespread lesions
Management
- Salicylic acid shampoo (Sebulex) OR
- Application of mineral oil followed by washing and removal of scales with comb
- Avoid topical steroids
Disposition
- Outpatient