Hepatomegaly: Difference between revisions
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[File:Liver measurements on ultrasonography.jpg|thumb|Evaluating liver size on ultrasound.]] | [[File:Liver measurements on ultrasonography.jpg|thumb|Evaluating liver size on ultrasound.]] | ||
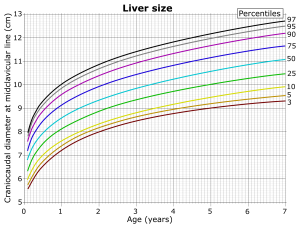
[[File:Liver size at the midclavicular line at 0 to 7 years.png|thumb|Pediatric liver size percentiles.]] | [[File:Liver size at the midclavicular line at 0 to 7 years.png|thumb|Pediatric liver size percentiles.]] | ||
[[File:Se000.jpg|thumb||Hepatomegaly on CT.]] | |||
*Evaluate for etiology; depending on presentation, workup may include: | *Evaluate for etiology; depending on presentation, workup may include: | ||
**[[LFTs]], coags | **[[LFTs]], coags | ||
Revision as of 22:50, 13 November 2024
Background
- Big liver
- Caused by infection, tumours, metabolic disorders, drugs
Clinical Features
- Palpable (or radiologically appreciated) enlarged liver
- +/- stigmata of hepatic dysfunction
- +/- signs of causative pathology
Differential Diagnosis
Hepatic Dysfunction
Infectious
- Hepatitis
- Malaria
- HIV (present in 50% of AIDS patients)[1]
- EBV
- Babesiosis, leptospirosis
- Typhoid
- Hepatic abscess, amebiasis
Neoplastic
Metabolic
Biliary
- Biliary cirrhosis
Drugs
- Alcoholic cirrhosis
- Alcoholic hepatitis
- Hepatotoxic drugs
Miscellaneous
- Other causes of cirrhosis
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Veno-occlusive disease
- CHF (right heart failure)
Evaluation
- Evaluate for etiology; depending on presentation, workup may include:
- LFTs, coags
- CBC, BMP
- RUQ US
- Acute hepatitis serologies, other infectious workup as indicated
- Acetaminophen levels, tox panel
- CHF workup if suspect right heart failure
- GI consult
Management
- Treat underlying condition
- Treat hepatic dysfunction, if present
Disposition
- Dependant on presentation; consider GI follow up if discharging and hepatomegaly not previously noted
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Tintanelli's