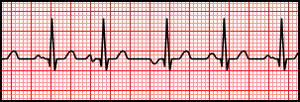Multifocal atrial tachycardia: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "==Background== ===Causes=== *COPD *CHF *Sepsis *Methylxanthine toxicity ==Clinical Features== ==Differential Diagnosis== ==Workup== ==Management== ==Disposi...") |
(→Causes) |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
[[File:Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia.svg|thumb|Rhythm strip of multifocal atrial tachycardia.]] | |||
*Multiple (3 or more) ectopic foci in the atria causing an irregular atrial tachycardia | |||
*Increased automaticity due to causes listed below | |||
===Causes=== | ===Causes=== | ||
| Line 5: | Line 8: | ||
*[[CHF]] | *[[CHF]] | ||
*[[Sepsis]] | *[[Sepsis]] | ||
*Methylxanthine toxicity | *[[Methylxanthine toxicity]] / [[Theophylline toxicity]] | ||
*[[Electrolyte abnormalities]] | |||
*Other associations | |||
**[[Valvular heart disease]] | |||
**[[DM]] | |||
**[[Acute renal failure]] | |||
**Postoperative state | |||
**[[Pulmonary embolism]] | |||
**[[Pneumonia]] | |||
**[[Anemia]] | |||
**[[Digoxin toxicity]] | |||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
*[[Palpitations]] | |||
*[[Dyspnea]] | |||
*[[Chest pain]] | |||
*Presyncope/[[syncope]] | |||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
{{Tachycardia (narrow) DDX}} | |||
{{Palpitations DDX}} | |||
==Evaluation== | |||
== | [[File:Multifocal atrial tachycardia - MAT.png|thumb|Multifocal atrial tachycardia]] | ||
*[[ECG]] | |||
**Irregular tachycardia (>100 bpm) | |||
**At least 3 distinct p wave morphologies with different P-R intervals | |||
**No dominant pacemaker site | |||
*BMP, Magnesium | |||
*Hemoglobin/hematocrit | |||
*Consider infectious disease work up | |||
*Consider [[ABG]]/[[VBG]] | |||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
*Treat underlying cause | |||
*Replace [[magnesium]] | |||
*Replace [[potassium]] | |||
*Increased AV nodal activity is unlikely to be effective | |||
**[[Vagal maneuvers]] and [[adenosine]] may help reveal underlying rhythm/p-waves | |||
**Can consider [[beta-blocker]] or [[calcium channel blocker]] in hemodynamically stable patient | |||
***Use beta-blockers cautiously in patients with pulmonary disease | |||
*[[Cardioversion]] ''not'' definitive | |||
**MAT likely to recur if underlying etiology not addressed | |||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
*Disposition depends on underlying illness, but often requires admission due to illness severity | |||
*Poor prognostic sign when MAT develops during hospitalization or acute illness | |||
**60% in-hospital mortality | |||
***Due to illness, not arrhythmia | |||
**Mean survival around 1 year | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Dysrhythmias]] | |||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:13, 30 July 2025
Background
- Multiple (3 or more) ectopic foci in the atria causing an irregular atrial tachycardia
- Increased automaticity due to causes listed below
Causes
- COPD
- CHF
- Sepsis
- Methylxanthine toxicity / Theophylline toxicity
- Electrolyte abnormalities
- Other associations
- Valvular heart disease
- DM
- Acute renal failure
- Postoperative state
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pneumonia
- Anemia
- Digoxin toxicity
Clinical Features
- Palpitations
- Dyspnea
- Chest pain
- Presyncope/syncope
Differential Diagnosis
Narrow-complex tachycardia
- Regular
- AV Node Independent
- Sinus tachycardia
- Atrial tachycardia (uni-focal or multi-focal)
- Atrial fibrillation
- Atrial flutter
- Idiopathic fascicular left ventricular tachycardia
- AV Node Dependent
- AV Node Independent
- Irregular
- Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT)
- Sinus tachycardia with frequent PACs, PJCs, PVCs
- Atrial fibrillation
- Atrial flutter with variable conduction
- Digoxin Toxicity
Palpitations
- Arrhythmias:
- Non-arrhythmic cardiac causes:
- Psychiatric causes:
- Drugs and Medications:
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
- Drugs of abuse (e.g. cocaine)
- Medications (e.g. digoxin, theophylline)
- Tobacco
- Misc
Evaluation
- ECG
- Irregular tachycardia (>100 bpm)
- At least 3 distinct p wave morphologies with different P-R intervals
- No dominant pacemaker site
- BMP, Magnesium
- Hemoglobin/hematocrit
- Consider infectious disease work up
- Consider ABG/VBG
Management
- Treat underlying cause
- Replace magnesium
- Replace potassium
- Increased AV nodal activity is unlikely to be effective
- Vagal maneuvers and adenosine may help reveal underlying rhythm/p-waves
- Can consider beta-blocker or calcium channel blocker in hemodynamically stable patient
- Use beta-blockers cautiously in patients with pulmonary disease
- Cardioversion not definitive
- MAT likely to recur if underlying etiology not addressed
Disposition
- Disposition depends on underlying illness, but often requires admission due to illness severity
- Poor prognostic sign when MAT develops during hospitalization or acute illness
- 60% in-hospital mortality
- Due to illness, not arrhythmia
- Mean survival around 1 year
- 60% in-hospital mortality