Hemoptysis: Difference between revisions
| (44 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | ==Background== | ||
*Coughing of blood that originates from respiratory tract below level of larynx | |||
*Death usually occurs from asphyxiation, not exanguination | |||
*Easy to confuse with [[epistaxis]] or oropharynx bleeding | |||
== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
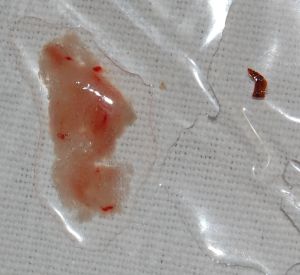
[[File:Krev na gázových čtvercích.jpg|thumb|Example of hemoptysis from coughing into gauze.]] | |||
[[File:Raetchon å sonk.jpg|thumb|Example of hemoptysis upon bronchial lavage.]] | |||
*Coughing up blood | |||
==Differential Diagnosis== | |||
*[[Epistaxis]] | |||
*Oropharynx bleeding | |||
*[[Hematemesis]] | |||
{{Hemoptysis DDX}} | |||
==Evaluation== | |||
===Workup=== | |||
*Imaging | |||
**[[CXR]] | |||
***Nml in 30% (most of whom end up having bronchitis) | |||
**Chest CT with IV contrast | |||
***Indicated for gross hemoptysis or suspicious CXR | |||
**Bronchoscopy | |||
*Labs | |||
**CBC | |||
**Coags | |||
**Sputum stain/culture | |||
**Chem (Cr) | |||
**T&S/T&C | |||
**[[Urinalysis]] (autoimmune) | |||
**[[ECG]] (pulmonary hypertension/PE) | |||
===Evaluation=== | |||
*Massive = A single expectoration of ≥ 50cc '''OR''' >600cc/24h | |||
**Rare, occurring in 1-5% of patients. | |||
*May differentiate from hematemesis with pH litmus paper | |||
**Hemoptysis tends to be alkaline | |||
**[[Hematemesis]] tends to be acidic, and stomach acid tends to turn bright red blood in stomach to brown/black fragments unless massive | |||
==Management== | |||
*Patient Placement | |||
**Placing patient with affected lung down may actually worsen V-Q mismatch | |||
**Some advocate for prone positioning | |||
*[[Intubation]] | |||
**Use 8-0 tube to allow for subsequent bronchoscopy | |||
**If possible can selectively intubate the unaffected bronchus to prevent aspiration | |||
***After tube passes through cords rotate 90degrees left or right and advance | |||
****Can also use ''coude'' tip of [[bougie]]<ref>Gottlieb M, Sharma V, Field J, Rozum M, Bailitz J. Utilization of a gum elastic bougie to facilitate single lung intubation. Am J Emerg Med. 2016 Dec;34(12):2408-2410. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2016.08.057. Epub 2016 Aug 27. PMID: 27614374.</ref> | |||
*Coagulopathy | |||
**[[FFP]] | |||
*Emergent bronchoscopy or embolization for life-threatening hemorrhage | |||
*Nebulized [[TXA]] 500 mg tid<ref>Wand O, et al. Inhaled Tranexamic Acid for Hemoptysis Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Chest. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2018.09.026</ref> | |||
**Pediatric: used in [https://www.emrap.org/episode/emrap2018june/case report] | |||
*IV [[TXA]] may reduce in-hospital mortality, length of stay, and total healthcare costs<ref>Kinoshita T, Ohbe H, Matsui H, Fushimi K, Ogura H, Yasunaga H. Effect of tranexamic acid on mortality in patients with haemoptysis: a nationwide study. Crit Care. 2019;23(1):347. Published 2019 Nov 6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6836388/</ref> | |||
**Absolute in-hospital mortality reduction was 2.5% in the retrospective study of nearly 20,000 patients | |||
**No particular dosing regimen, but in this study, no association was found between TXA and seizures, in part per the authors, due to most patients receiving no more than 2 g of TXA total | |||
===Massive=== | |||
*Angle head down with affected lung low | |||
*Consider angio embolization | |||
*Consider [[intubation]] with >8.0 (for bronch) | |||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
*Gross hemoptysis: | |||
**Admit | |||
*Young patient (<40yr) with scant hemoptysis, normal [[CXR]], no smoking history: | |||
**Discharge | |||
*Risk factors for neoplasm (even if CXR normal) or suspicious CXR: | |||
**Discuss with pulmonologist before discharge | |||
[[Category: | ==References== | ||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:Pulmonary]] | |||
[[Category:Symptoms]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:40, 24 April 2024
Background
- Coughing of blood that originates from respiratory tract below level of larynx
- Death usually occurs from asphyxiation, not exanguination
- Easy to confuse with epistaxis or oropharynx bleeding
Clinical Features
- Coughing up blood
Differential Diagnosis
- Epistaxis
- Oropharynx bleeding
- Hematemesis
Hemoptysis
- Infectious
- Neoplastic
- Lung cancer
- Metastatic cancer
- Cardiovascular
- Pulmonary embolism
- Congestive heart failure
- Pulmonary hypertension
- AV malformation
- Mitral stenosis
- Alveolar hemorrhage syndromes
- Hematologic
- Uremia
- Platelet dysfunction (ASA, clopidogrel)
- Anticoagulant therapy
- Traumatic
- Foreign body aspiration
- Ruptured bronchus
- Inflammatory
- Miscellaneous
- Cocaine inhalation (crack lung)
- Catamenial pneumothorax
- Goodpasture syndrome
- Cystic fibrosis
- Epistaxis
- Blood-laced mucus from the sinus or nose area
- Upper GI bleeding
Evaluation
Workup
- Imaging
- CXR
- Nml in 30% (most of whom end up having bronchitis)
- Chest CT with IV contrast
- Indicated for gross hemoptysis or suspicious CXR
- Bronchoscopy
- CXR
- Labs
- CBC
- Coags
- Sputum stain/culture
- Chem (Cr)
- T&S/T&C
- Urinalysis (autoimmune)
- ECG (pulmonary hypertension/PE)
Evaluation
- Massive = A single expectoration of ≥ 50cc OR >600cc/24h
- Rare, occurring in 1-5% of patients.
- May differentiate from hematemesis with pH litmus paper
- Hemoptysis tends to be alkaline
- Hematemesis tends to be acidic, and stomach acid tends to turn bright red blood in stomach to brown/black fragments unless massive
Management
- Patient Placement
- Placing patient with affected lung down may actually worsen V-Q mismatch
- Some advocate for prone positioning
- Intubation
- Coagulopathy
- Emergent bronchoscopy or embolization for life-threatening hemorrhage
- Nebulized TXA 500 mg tid[2]
- Pediatric: used in report
- IV TXA may reduce in-hospital mortality, length of stay, and total healthcare costs[3]
- Absolute in-hospital mortality reduction was 2.5% in the retrospective study of nearly 20,000 patients
- No particular dosing regimen, but in this study, no association was found between TXA and seizures, in part per the authors, due to most patients receiving no more than 2 g of TXA total
Massive
- Angle head down with affected lung low
- Consider angio embolization
- Consider intubation with >8.0 (for bronch)
Disposition
- Gross hemoptysis:
- Admit
- Young patient (<40yr) with scant hemoptysis, normal CXR, no smoking history:
- Discharge
- Risk factors for neoplasm (even if CXR normal) or suspicious CXR:
- Discuss with pulmonologist before discharge
References
- ↑ Gottlieb M, Sharma V, Field J, Rozum M, Bailitz J. Utilization of a gum elastic bougie to facilitate single lung intubation. Am J Emerg Med. 2016 Dec;34(12):2408-2410. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2016.08.057. Epub 2016 Aug 27. PMID: 27614374.
- ↑ Wand O, et al. Inhaled Tranexamic Acid for Hemoptysis Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Chest. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2018.09.026
- ↑ Kinoshita T, Ohbe H, Matsui H, Fushimi K, Ogura H, Yasunaga H. Effect of tranexamic acid on mortality in patients with haemoptysis: a nationwide study. Crit Care. 2019;23(1):347. Published 2019 Nov 6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6836388/