Skin abscess: Difference between revisions
Neil.m.young (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Neil.m.young (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
[[Incision and drainage]] | [[Incision and drainage]] | ||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
*[http://emcrit.org/emnerd/case-pragmatic-wound/ EMNerd Case of the Pragmatic Wound] | |||
*[http://www.emlitofnote.com/2016/03/are-antibiotics-back-in-favor-for.html Are Antibiotics Back in Favor for Abscesses?] | |||
*[http://www.sonoguide.com/abscess.html Sonoguide: Abscess Assessment] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 20:43, 2 June 2016
Background
Clinical Features
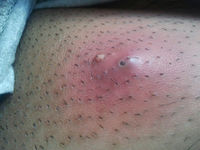
- Tender nodular region with surrounding induration
- Fluctuance
- Surrounding erythema
Differential Diagnosis
- Cyst
- Vascular malformation
Skin and Soft Tissue Infection
- Cellulitis
- Erysipelas
- Lymphangitis
- Folliculitis
- Hidradenitis suppurativa
- Skin abscess
- Necrotizing soft tissue infections
- Mycobacterium marinum
Look-A-Likes
- Sporotrichosis
- Osteomyelitis
- Deep venous thrombosis
- Pyomyositis
- Purple glove syndrome
- Tuberculosis (tuberculous inflammation of the skin)
Diagnosis
- Clinical exam
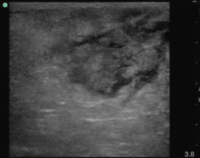
- Soft tissue ultrasound can differentiate between abscess and cellulitis
- Assess for fluid collection and swirl within the collection
Management
- Incision and drainage
- Antibiotics
- Despite withholding aantbiotics is part of Choosing wisely ACEP new evidence suggest abx NNT of 14 to prevent 1 treatment failure[4]
- TMP/SMX x 5 days (all abscesses)[5]
- Consider more aggressive antibiotic treatment if concomitant cellulitis
Disposition
See Also
External Links
- EMNerd Case of the Pragmatic Wound
- Are Antibiotics Back in Favor for Abscesses?
- Sonoguide: Abscess Assessment
References
- ↑ Maligner D et al. The prevalence of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) in skin abscesses presenting to the pediatric emergency department. N C Med J. 2008 Sep-Oct;69(5):351-4.
- ↑ Pickett A et al. Changing incidence of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus skin abscesses in a pediatric emergency department. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2009 Dec;25(12):831-4.
- ↑ Bradley W. Frazee et al. High Prevalence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Emergency Department Skin and Soft Tissue Infections http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2004.10.011
- ↑ Talan DA, et al. Trimethoprim–Sulfamethoxazole versus placebo for uncomplicated skin abscess. NEJM. 2016; 374(9):823-832.
- ↑ EBQ:TMP-SMX vs Placebo for Uncomplicated Skin Abscess