Osteoarthritis: Difference between revisions
Neil.m.young (talk | contribs) (format) |
|||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
===Nonpharmacological=== | ===Nonpharmacological=== | ||
* | *Weight loss | ||
* | *Ice/warm packs | ||
* | *Physical therapy | ||
* | *Occupational therapy | ||
* | *Exercise | ||
===Pharmacological <ref> Jordan JM, et al. Prevalence of knee symptoms and radiographic and symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in African Americans and Caucasians: the Johnston County Osteoarthritis Project. J Rheumatol. 2007 Jan. 34(1):172-80. </ref>=== | ===Pharmacological <ref> Jordan JM, et al. Prevalence of knee symptoms and radiographic and symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in African Americans and Caucasians: the Johnston County Osteoarthritis Project. J Rheumatol. 2007 Jan. 34(1):172-80. </ref>=== | ||
* | *Topical capsaicin | ||
* | *Topical [[NSAIDs]] | ||
* | *Oral [[NSAIDs]] | ||
*Tylenol | *Tylenol | ||
* | *Steroid injections | ||
*Tramadol | *Tramadol | ||
===Surgical=== | ===Surgical=== | ||
* | *Arthroscopy for removal of meniscal tears or loose foreign bodies | ||
** | **No additional benefit compared to PT and medical therapy in routine OA <ref> Kirkley A, et al. A randomized trial of arthroscopic surgery for osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2008 Sep 11. 359(11):1097-107 </ref> | ||
* | *Osteotomy in young patients with misalignment of knee or hip joint | ||
* | *Arthroplasty | ||
** | **If all other modalities are ineffective | ||
** | **Prothetic knee/hip/shoulder usually has 10-15 year viability | ||
** | **Infection, [[Pulmonary embolism]] are biggest risks | ||
* | *Joint fusion | ||
** | **Relieves pain but prevents motion | ||
** | **May be used in small foot/ankle bones or after failed arthroplasties | ||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
Revision as of 20:47, 4 September 2015
Background
Risk Factors
- Age
- Female versus male sex
- Obesity
- Lack of osteoporosis
- Occupation
- Previous injury
- Muscle weakness
- Genetic elements
Clinical Features
- Commonly affected joints
- Cervical and lumbar spine
- First carpometacarpal joint
- Proximal interphalangeal joint
- Distal interphalangeal joint
- Hip
- Knee
- Subtalar joint
- First metatarsophalangeal joint
- Uncommonly affected joints
- Shoulder
- Wrist
- Elbow
- Metacarpophalangeal joint
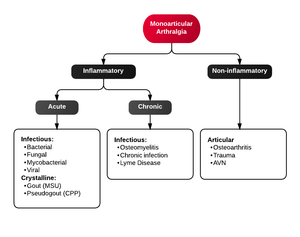
Differential Diagnosis
Monoarticular arthritis
- Acute osteoarthritis
- Avascular necrosis
- Crystal-induced (Gout, Pseudogout)
- Gonococcal arthritis, arthritis-dermatitis syndrome
- Nongonococcal septic arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Malignancy (metastases, osteochondroma, osteoid osteoma)
- Reactive poststreptococcal arthritis
- Trauma-induced arthritis
- Fracture
- Ligamentous injury
- Overuse
- Avascular necrosis
- Decompression sickness
- Spontaneous osteonecrosis
- Hemorrhagic (e.g. hemophilia, systemic anticoagulation
- Seronegative spondyloarthropathies (ankylosing spondylitis, IBD, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis
- RA, SLE
- Sarcoidosis, amyloidosis
- Periarticular pathology
- Transient (Toxic) Synovitis (Hip)
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)
- Legg Calve Perthes Disease
Polyarthritis
- Fibromyalgia
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reactive poststreptococcal arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatic fever
- Serum sickness
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Serum sickness–like reactions
- Viral arthritis
Diagnosis
- Greater than 50 years of age
- Morning stiffness for less than 30 minutes
- Crepitus on active motion of the knee
- Bony tenderness
- Bony enlargement
- No palpable warmth
Management
Nonpharmacological
- Weight loss
- Ice/warm packs
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Exercise
Pharmacological [1]
Surgical
- Arthroscopy for removal of meniscal tears or loose foreign bodies
- No additional benefit compared to PT and medical therapy in routine OA [2]
- Osteotomy in young patients with misalignment of knee or hip joint
- Arthroplasty
- If all other modalities are ineffective
- Prothetic knee/hip/shoulder usually has 10-15 year viability
- Infection, Pulmonary embolism are biggest risks
- Joint fusion
- Relieves pain but prevents motion
- May be used in small foot/ankle bones or after failed arthroplasties
Disposition
- Home with PMD follow up
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Jordan JM, et al. Prevalence of knee symptoms and radiographic and symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in African Americans and Caucasians: the Johnston County Osteoarthritis Project. J Rheumatol. 2007 Jan. 34(1):172-80.
- ↑ Kirkley A, et al. A randomized trial of arthroscopic surgery for osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2008 Sep 11. 359(11):1097-107