Septic arthritis: Difference between revisions
Neil.m.young (talk | contribs) (Text replacement - " pt " to " patient ") |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''This page is for <u>adult</u> patients; for pediatric patients see [[septic arthritis (peds)]].'' | |||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
*Most important diagnostic consideration in acute joint pain (can destroy joint in days) | *Most important diagnostic consideration in acute joint pain (can destroy joint in days) | ||
*Knee most commonly involved in adults; hip most common in | *Knee most commonly involved in adults; hip most common in pediatric | ||
*Most often seen in patients | *Most often seen in patients >65yr | ||
*Most common causative organisms | *Most common causative organisms | ||
**<35 y/o ''[[N. gonorrhoeae]]'' | **<35 y/o ''[[N. gonorrhoeae]]'' | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
**May have prodromal phase: | **May have prodromal phase: | ||
***Migratory arthritis and tenosynovitis predominate before pain and swelling occurs | ***Migratory arthritis and tenosynovitis predominate before pain and swelling occurs | ||
***Macularpapular rash or pustules | ***Macularpapular rash or pustules especially on hands/feet may proceed overt arthritis | ||
*Endocarditis should be considered in the presence of 2 or more affected joints | *Endocarditis should be considered in the presence of 2 or more affected joints | ||
| Line 30: | Line 31: | ||
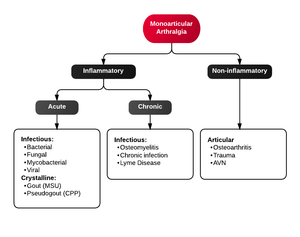
{{Differential Diagnosis Monoarthritis}} | {{Differential Diagnosis Monoarthritis}} | ||
== | ==Evaluation<ref>Carpenter CR, Schuur JD, Everett WW, Pines JM. Evidence-based diagnostics: adult septic arthritis. Acad Emerg Med. 2011;18(8):781-96.</ref>== | ||
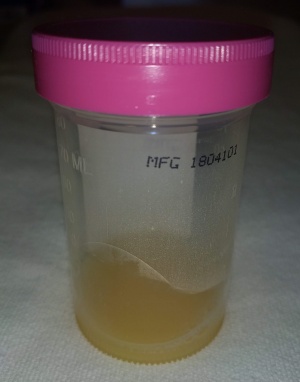
[[File:SepticJointFluid.jpg|thumb|Synovial fluid from a septic knee]] | |||
===Work-Up=== | ===Work-Up=== | ||
*Arthrocentesis with synovial fluid analysis | *Arthrocentesis with synovial fluid analysis | ||
** | **cell count with differential | ||
**glucose | |||
**protein | |||
**bacterial culture and sensitivity (not 100% sn) | |||
**polarized light microscopy for crystals | |||
*CBC | *CBC | ||
*ESR | *ESR - Sn 94% (with 15mm/h cut-off)<ref>Hariharan, H, et al. Sensitivity of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and C-reactive Protein for the Exclusion of Septic Arthritis in Emergency Department Patients. J of Emerg Med. 2010; 40(4):428–431. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2010.05.029</ref> | ||
*CRP - Sn 92% (with 20mg/L cut-off) | |||
*CRP | |||
*Blood Culture | *Blood Culture | ||
*Gonorrhea culture (urethral/cervical/pharyngeal/rectal) | *Gonorrhea culture (urethral/cervical/pharyngeal/rectal) | ||
*Imaging | *Imaging (may be helpful for excluding other diagnoses - e.g. trauma, osteo, etc) | ||
*Immunocompromised | *Immunocompromised | ||
**Consider mycobacterial or fungal arthritis | **Consider mycobacterial or fungal arthritis | ||
**Leukemia history: predisposed to Aeromonas infections | **Leukemia history: predisposed to Aeromonas infections | ||
*Periprosthetic infection | |||
**Non-emergent: acute microbiological diagnosis is more important than rapid antibiotics | |||
**Diagnose with two synovial fluid cultures (avoid collection from a draining sinus) | |||
**CRP >100mg/L during first 6 weeks post-op warrants aspiration and may be used to differentiate from superficial skin infection | |||
{{Arthrocentesis diagnostic chart}} | {{Arthrocentesis diagnostic chart}} | ||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
===[[Antibiotics]]=== | ===[[Antibiotics]]=== | ||
{{Septic Arthritis Antibiotics}} | {{Septic Arthritis Antibiotics}} | ||
===Consultation=== | ===Consultation=== | ||
*Consult ortho for joint irrigation in OR if joint aspirate is indicative of infection | *Consult ortho for joint irrigation in OR if joint aspirate is indicative of infection | ||
**Benefit of serial aspirations vs arthroscopy vs irrigation and debridement is unclear | |||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
*Admit all | *Admit all | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Arthrocentesis]] | *[[Arthrocentesis]] | ||
*[[Monoarticular | *[[Monoarticular arthritis]] | ||
*[[Septic | *[[Septic arthritis of the hip (peds)]] | ||
*[[Septic | *[[Septic arthritis (peds)]] | ||
*[[Knee | *[[Knee diagnoses]] | ||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
| Line 71: | Line 78: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:ID]] [[Category:Orthopedics]] | [[Category:ID]] | ||
[[Category:Orthopedics]] | |||
Latest revision as of 03:31, 11 December 2019
This page is for adult patients; for pediatric patients see septic arthritis (peds).
Background
- Most important diagnostic consideration in acute joint pain (can destroy joint in days)
- Knee most commonly involved in adults; hip most common in pediatric
- Most often seen in patients >65yr
- Most common causative organisms
- <35 y/o N. gonorrhoeae
- >35 y/o S. aureus
Clinical Features
- Fever
- Warm, red, painful, swollen joint
- Decreased range of motion to active and passive movement
- Gonococcal arthritis
- Urethritis/vaginitis may be absent
- May have prodromal phase:
- Migratory arthritis and tenosynovitis predominate before pain and swelling occurs
- Macularpapular rash or pustules especially on hands/feet may proceed overt arthritis
- Endocarditis should be considered in the presence of 2 or more affected joints
Differential Diagnosis
- Transient (Toxic) Synovitis
- Abscess
- Cellulitis
- Primary rheumatologic disorder (i.e. vasculitis)
- Iatrogenic
- Reactive Arthritis (Poststreptococcal)
- Consider if patient has Sickle Cell (fever and limited joint ROM)
- Osteomyelitis typically has neither
Monoarticular arthritis
- Acute osteoarthritis
- Avascular necrosis
- Crystal-induced (Gout, Pseudogout)
- Gonococcal arthritis, arthritis-dermatitis syndrome
- Nongonococcal septic arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Malignancy (metastases, osteochondroma, osteoid osteoma)
- Reactive poststreptococcal arthritis
- Trauma-induced arthritis
- Fracture
- Ligamentous injury
- Overuse
- Avascular necrosis
- Decompression sickness
- Spontaneous osteonecrosis
- Hemorrhagic (e.g. hemophilia, systemic anticoagulation
- Seronegative spondyloarthropathies (ankylosing spondylitis, IBD, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis
- RA, SLE
- Sarcoidosis, amyloidosis
- Periarticular pathology
- Transient (Toxic) Synovitis (Hip)
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)
- Legg Calve Perthes Disease
Evaluation[1]
Work-Up
- Arthrocentesis with synovial fluid analysis
- cell count with differential
- glucose
- protein
- bacterial culture and sensitivity (not 100% sn)
- polarized light microscopy for crystals
- CBC
- ESR - Sn 94% (with 15mm/h cut-off)[2]
- CRP - Sn 92% (with 20mg/L cut-off)
- Blood Culture
- Gonorrhea culture (urethral/cervical/pharyngeal/rectal)
- Imaging (may be helpful for excluding other diagnoses - e.g. trauma, osteo, etc)
- Immunocompromised
- Consider mycobacterial or fungal arthritis
- Leukemia history: predisposed to Aeromonas infections
- Periprosthetic infection
- Non-emergent: acute microbiological diagnosis is more important than rapid antibiotics
- Diagnose with two synovial fluid cultures (avoid collection from a draining sinus)
- CRP >100mg/L during first 6 weeks post-op warrants aspiration and may be used to differentiate from superficial skin infection
Template:Arthrocentesis diagnostic chart
Management
Antibiotics
For adults treatment should be divided into Gonococcal and Non-Gonococcal
Gonococcal
- Ceftriaxone 1g IV once daily
- Cefixime 400 mg PO BID is an option for outpatient therapy after initial 3 days of Ceftriaxone
Non-Gonococcal
- Treatment should cover S. aureus, Streptococcus, Pseudomonas, Enterococcus, B. burgdorferi
- Vancomycin 15-20 mg/kg IV BID PLUS any of the following:
- Ceftriaxone 2g IV once daily
- Cefepime 2g IV three times daily
- Ceftazidime 2g IV three times daily
- Ciprofloxacin 400mg IV three times daily
Pediatrics
- Ceftriaxone 1g IV once daily
Sickle Cell
Coverage for Salmonella and Staphylococcus spp
- Vancomycin 20mg/kg IV twice daily PLUS
- Ciprofloxacin 400mg IV three times daily OR
- Imipenem/cilastatin 1g IV three times daily
Consultation
- Consult ortho for joint irrigation in OR if joint aspirate is indicative of infection
- Benefit of serial aspirations vs arthroscopy vs irrigation and debridement is unclear
Disposition
- Admit all
See Also
- Arthrocentesis
- Monoarticular arthritis
- Septic arthritis of the hip (peds)
- Septic arthritis (peds)
- Knee diagnoses
External Links
References
- ↑ Carpenter CR, Schuur JD, Everett WW, Pines JM. Evidence-based diagnostics: adult septic arthritis. Acad Emerg Med. 2011;18(8):781-96.
- ↑ Hariharan, H, et al. Sensitivity of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and C-reactive Protein for the Exclusion of Septic Arthritis in Emergency Department Patients. J of Emerg Med. 2010; 40(4):428–431. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2010.05.029